Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):82-90 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.034
Meta-analysis study on anesthetic sedation recovery and onset times in pediatric and elderly patients undergoing CT and MRI
- 1 Department of Anesthesiology, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, No. 105 Jiefang Road, Jinan City, 250013 Jinan, P. R. China
- 2 Department of Anesthesiology, Jinan Third People's Hospital, No. 1 Wangsheren North Street, Gongye North Road, Licheng District, Jinan City, Shandong Province, 250132, P. R. China
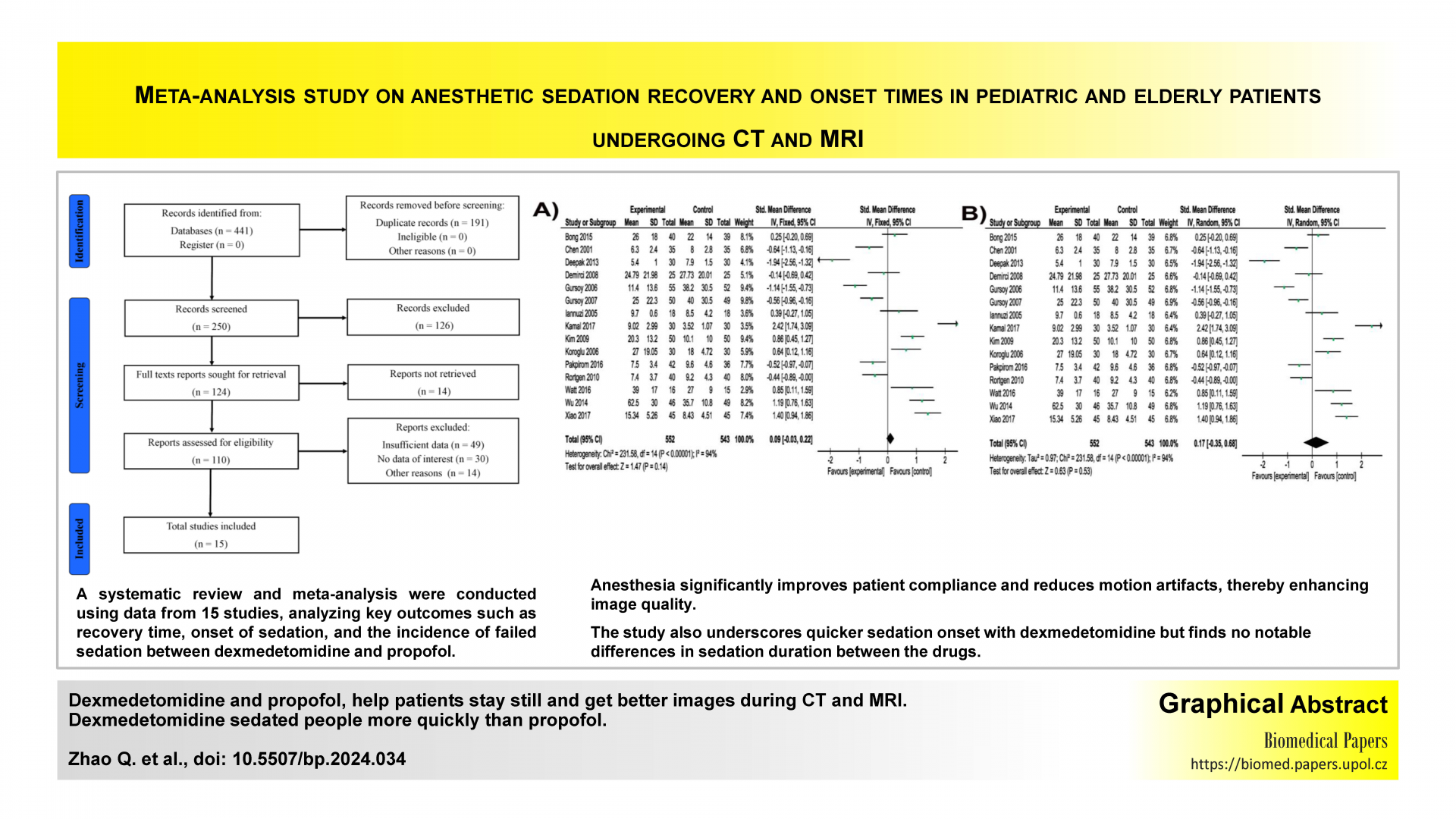
Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are crucial diagnostic modalities that require patients to remain immobile for extended periods, with anesthesia sometimes used for comfort and image quality enhancement. The study compares dexmedetomidine and propofol in reducing recovery time and sedation onset in pediatric and elderly patients undergoing CT and MRI procedures. A meta-analysis of fifteen studies assessing recovery time, sedation onset, and failed sedation between dexmedetomidine and propofol in pediatric and elderly patients during CT and MRI was conducted. The study indicated that the administration of anaesthesia markedly improved patient compliance and reduced motion artefacts in both CT and MRI (P<0.00001, I2=94%). The meta-analysis indicated that the mean difference (MD) in the onset of sedation was significantly faster in the control group (P<0.00001, I2=96%). The study reveals that dexmedetomidine and propofol anesthesia can improve patient image quality during CT and MRI procedures by reducing motion artefacts. Dexmedetomidine sedated people more quickly than propofol, but no significant differences in sedation duration were observed.
Keywords: anesthesia, elderly patients, pediatric patients, propofol, dexmedetomidine, CT scan, meta-analysis, recovery time
Received: June 25, 2024; Revised: September 24, 2024; Accepted: October 11, 2024; Prepublished online: November 1, 2024; Published: June 1, 2025 Show citation
| ACS | AIP | APA | ASA | Harvard | Chicago | Chicago Notes | IEEE | ISO690 | MLA | NLM | Turabian | Vancouver |
References
- . Jung SM. Drug selection for sedation and general anesthesia in children undergoing ambulatory magnetic resonance imaging. Yeungnam Univ J Med 2020;37(3):159-68.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Arlachov Y, Ganatra RH. Sedation/anaesthesia in paediatric radiology. Br J Radiol 2012;85(1019):e1018-31.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Shankar VR. Sedating children for radiological procedures: an intensivist's perspective. Pediatr Radiol 2008;38 Suppl 2:S213-7.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Schulte-Uentrop L, Goepfert MS. Anaesthesia or sedation for MRI in children. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 2010;23(4):513-7.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Artunduaga M, Liu CA, Morin CE. Safety challenges related to the use of sedation and general anesthesia in pediatric patients undergoing magnetic resonance imaging examinations. Pediatr Radiol 2021;51:724-35.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Michaud V, Morel B, Adamsbaum C, Bruneau B, Lenoir M, Petit P, Leiber LM, Blondiaux E, Brunereau L, Remérand F, Brisse HJ, Laffon M. French survey of sedation practices for pediatric magnetic resonance and computed tomography imaging. Pediatr Radiol 2023;53(8):1669-74.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Jevdjić J, Surbatović M, Drakulić-Miletić S, Zunić F. Deep sedation with midazolam and propofol in children undergoing ambulatory magnetic resonance imaging of the brain. Vojnosanit Pregl 2011;68(10):842-5. (In Serbian)
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Lieblich S. Preoperative Evaluation and Patient Selection for Office-Based Oral Surgery Anesthesia. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 2018;30(2):137-44.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Lau L, Jan G, Chan TF. Preparation of patients for anaesthesia - achieving quality care. Hong Kong Med J 2002;8(2):99-105.
- . Bailey MA, Saraswatula A, Dale G, Softley L (2016) Paediatric sedation for imaging is safe and effective in a district general hospital. Br J Radiol, 89(1061):20150483.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Youn AM, Ko YK, Kim YH. Anesthesia and sedation outside of the operating room. Korean J Anesthesiol 2015;68(4):323-31.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Bong CL, Lim E, Allen JC, Choo WL, Siow YN, Teo PB, Tan JS. A comparison of single-dose dexmedetomidine or propofol on the incidence of emergence delirium in children undergoing general anaesthesia for magnetic resonance imaging. Anaesthesia 2015;70:393-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Chen X, Zhao M, White PF, Li S, Tang J, Wender RH, Sloninsky A, Naruse R, Kariger R, Webb T, Norel E. The recovery of cognitive function after general anesthesia in elderly patients: a comparison of desflurane and sevoflurane. Anesth Analg 2001;93:1489-94.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Deepak TS, Vadlamani S, Kumar KS, Kempegowda P.Post-operative cognitive functions after general anesthesia with sevoflurane and desflurane in South Asian elderly. Middle East J Anaesthesiol 2013;22:143-8.
- . Demirci H, Erdamar H, Karakoc A. Thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsy: is topical local anaesthesia beneficial? Int J Clin Pract 2010;64(1):25-8.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Gursoy A, Ertugrul DT, Sahin M. Needle-free delivery of Lidocaine for reducing the pain associated with the fine-needle aspiration biopsy of Thyroid nodules: time-saving and efficacious procedure. Thyroid 2006;17:317-21.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Gursoy A, Ertugrul DT, Sahin M, Tutuncu NB, Demirer AN, Demirag NG. The analgesic efficacy of lidocaine/prilocaine (EMLA) cream during fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules. Clinical Endocrinol 2007;66(5):691-4.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Iannuzzi E, Iannuzzi M, Viola G, Cerulli A, Cirillo V, Chiefari M. Desflurane and sevoflurane in elderly patients during general anesthesia: a double blind comparison. Minerva Anestesiol 2005;71:147-55.
- . Kamal K, Asthana U, Bansal T, Dureja J, Ahlawat G, Kapoor S. Evaluation of efficacy of dexmedetomidine versus propofol for sedation in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. Saudi J Anaesth 2017;11:163-8.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Kim DW, Rho MH, Kim KN. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy of thyroid nodules: is it necessary to use local anesthesia for the application of one needle puncture? Korean J Radiol 2009;10(5):441-6.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Koroglu A, Demirbilek S, Teksan H, Sagir O, But AK, Ersoy MO. Sedative, haemodynamic and respiratory effects of dexmedetomidine in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging examination: Preliminary results. Br J Anaesth 2006;94:821-4.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Pakpirom J, Kraithep J, Pattaravit N. Length of postanesthetic care unit stay in elderly patients after general anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial comparing desflurane and sevoflurane. J Clin Anesth 2016;32:294-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Rortgen D, Kloos J, Fries M, Grottke O, Rex S, Rossaint R, Coburn M. Comparison of early cognitive function and recovery after desflurane or sevoflurane anaesthesia in the elderly: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Br J Anaesth 2010;104:167-74.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Watt S, Sabouri S, Hegazy R, Gupta P, Heard C. Does dexmedetomidine cause less airway collapse than propofol when used for deep sedation? J Clin Anesth 2016;35:259-67.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Wu J, Mahmoud M, Schmitt M, Hossain M, Kurth D. Comparison of propofol and dexmedetomedine techniques in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. Paediatr Anaesth 2014;24:813-18.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Xiao Y, He P, Jing G, Wang Q, Wen J. Comparison of sedative effect of dexmedetomide injection and propofol injection in pediatric patients undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. Zhongguo Lin Chuang Yao Li Xue Za Zhi 2017;33:1764-67.
- . Florkow MC, Willemsen K, Mascarenhas VV, Oei EHG, van Stralen M, Seevinck PR. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Versus Computed Tomography for Three-Dimensional Bone Imaging of Musculoskeletal Pathologies: A Review. J Magn Reson Imaging 2022;l56(1):11-34.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Cronin JA, Shen C, Rana S, Fricke ST, Matisoff A. Association Between Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Anesthetized Children and Hypothermia. Pediatr Qual Saf 2019;4(4):e181.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Wang X, Liu X, Mi J. Perioperative management and drug selection for sedated/anesthetized patients undergoing MRI examination: A review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023;102(16):e33592.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Lo C, Ormond G, McDougall R, Sheppard SJ, Davidson AJ. Effect of magnetic resonance imaging on core body temperature in anaesthetised children. Anaesth Intensive Care 2014;42(3):333-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . van Beek EJ, Leroy PL. Safe and effective procedural sedation for gastrointestinal endoscopy in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2012;54(2):171-85.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Uludağ Ö, Kaya R, Tutak A, Doğukan M, Çelik M, Dumlupinar E. Effect of Anesthesia Applied for Magnetic Resonance Imaging on the Body Temperature of Pediatric Patients. Cureus 2019;11(9):e5705.
- . Tobias JD, Leder M. Procedural sedation: A review of sedative agents, monitoring, and management of complications. Saudi J Anaesth 2011;5(4):395-410.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Alshuhri MS, Alkhateeb BA, Alomair OI, Alghamdi SA, Madkhali YA, Altamimi AM, Alashban YI, Alotaibi MM. Provision of Safe Anesthesia in Magnetic Resonance Environments: Degree of Compliance with International Guidelines in Saudi Arabia. Healthcare (Basel) 2023;10;11(18):2508.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Ruth MS, Sridharan N, Rai E, Joselyn AS. A prospective observational study to evaluate the magnitude of temperature changes in children undergoing elective MRI under general anesthesia. Saudi J Anaesth 2020;14(2):200-5.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed...
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original publication is properly cited. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.




