Biomedical papers, 2025 (vol. 169), issue 1
Reviews

Acute kidney injury due to gentamicin nephrotoxicity and specific miRNAs as biomarkers
Viktor Klementa, Nadezda Petejova, Pavel Horak, Ester Kurasova, Josef Zadrazil
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):1-8 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.031 
Acute kidney injury induced by gentamicin nephrotoxicity is a significant clinical concern due to the widespread use of gentamicin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Gentamicin can cause damage to renal tubular cells, leading to decreased kidney function. Emerging research highlights the role of specific microRNAs (miRNAs) as potential biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. These miRNAs are small, non-coding RNA molecules involved in regulating gene expression, and their altered levels in the blood or urine can indicate kidney damage before traditional markers, such as serum creatinine. Identifying these miRNAs could improve diagnosis, enable timely intervention, and potentially mitigate the adverse effects of gentamicin on renal health.
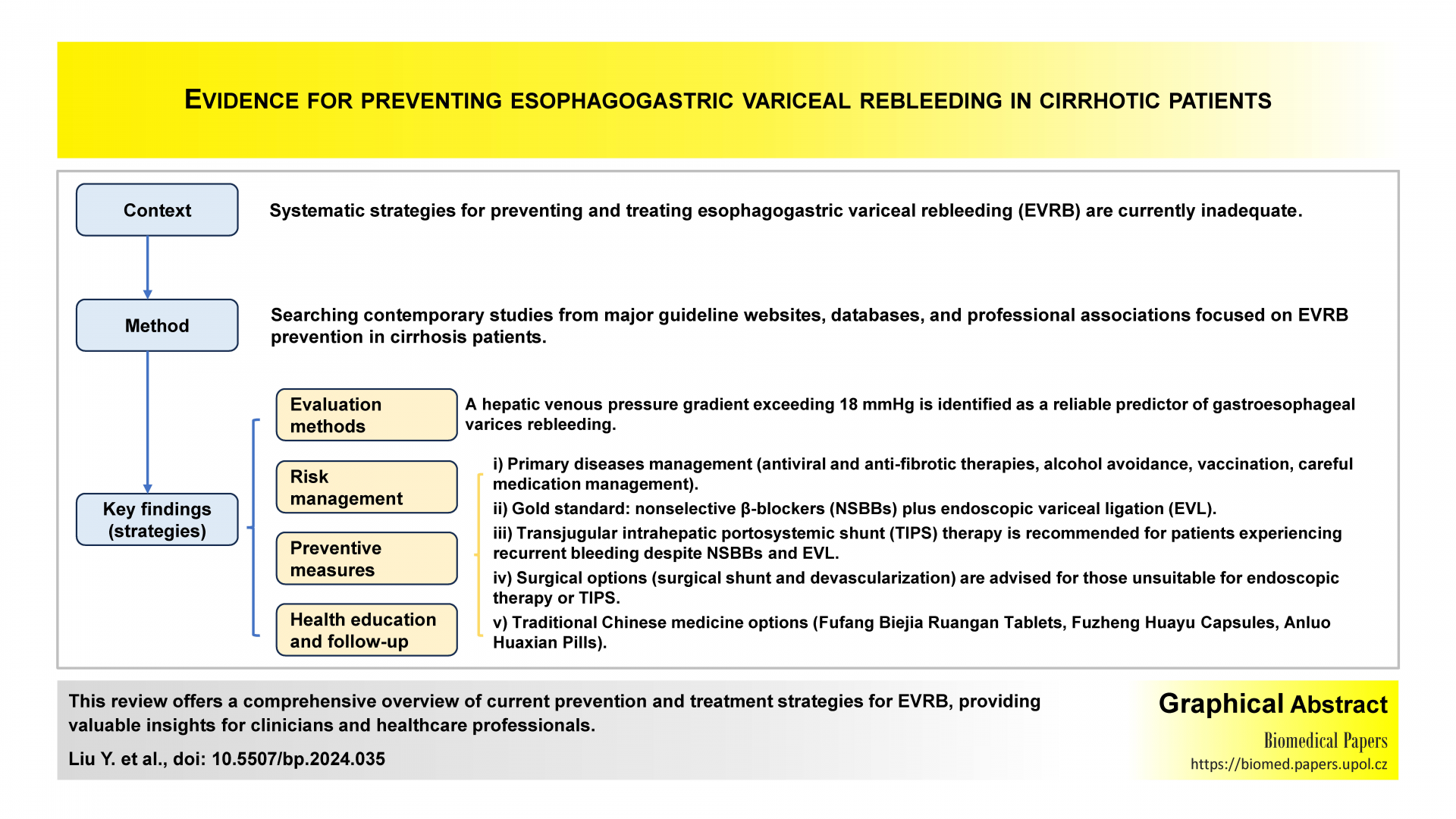
Evidence for preventing EVRB in cirrhotic patients: A systematic review
Ye Liu, Xiaoyan Wang, Yingjia Gu, Dan Niu
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):9-20 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.035 
The authors included publications up to July 1, 2023. Five guidelines, 1 systematic review, and 2 expert consensuses were included. Twenty-four of the best levels were summarized. The evidence includes evaluation methods, risk management, preventive measures, health education and follow-up. This systematic review summarizes the latest evidence of the best level of EVRB prevention in liver cirrhosis. These are practical and can be used as reference for clinical and medical personnel.
Original papers
Percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung lesions is a safe method associated with a very low risk of pleural recurrence
Martin Svaton, David Havel, Marcela Buresova, Jan Baxa, Petr Hosek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):21-25 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.030 
Percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung lesions is an alternative to bronchoscopic confirmation of lung lesions. The aim of this study was to assess the risk of pleural recurrence for all types of lung lesions. To the best of their knowledge, this has so far only been investigated in stage I lung tumors and not in all lung lesions. Secondary objectives included assessment of diagnostic yield and safety with respect to the incidence of pneumothorax and hemorrhage. In this study, percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung lesions showed high sensitivity and low degree of acute complications requiring an invasive solution. The risk of pleural recurrence after a biopsy was very low.
Clinical and molecular genetic analysis of cytologically uncertain thyroid nodules in patients with thyroid disease
Jindrich Lukas, Barbora Hintnausova, Vlasta Sykorova, Martin Syrucek, Marek Maly, David Lukas, Jaroslava Duskova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):26-31 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.048 
The study aimed to determine the preoperative clinical and molecular genetic risks of malignancy in indeterminate nodules (Bethesda III and IV) and their influence on the surgical treatment strategy of hemi/total thyroidectomy. Molecular tests were focused on the occurrence of pathogenic variants of somatic genes BRAF, RAS, TERT and rearrangements of RET/PTC, PAX8/PPARγ associated with thyroid oncogenesis. The incidence of clinical risk factors for malignancy was evaluated. The presence of at least one of these led to a significantly higher incidence of malignancy than in cases of their absence. From the experience of the authors so far, molecular genetic testing is one of the many decision-making factors in elective surgical procedures.
Results of surgical therapy of functioning pituitary adenomas
Vlastimil Novak, Lumir Hrabalek, Jan Schovanek, Zdenek Frysak, Racheal Temitope Ijisesan Perryova, Daniel Pohlodek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):32-36 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.037 
This study evaluates the results of surgical transnasal procedures in patients with functioning pituitary adenomas. The cohort consisted of 58 patients. Microadenoma was diagnosed in 58.6% and macroadenoma in 41.4%. In the group with excessive production of ACTH, complete remission was achieved after the first surgery in 78.6% of cases; in the group with excessive GH production in 51.4%. In the group with excessive production of PRL, it was 57.1%. Surgical therapy in the cohort described led to the normalisation of excessive hormone production in 58.6% of cases.
Impaired intestinal permeability in patients with multiple sclerosis
Lenka Fialova, Pavla Barilly, Ivana Stetkarova, Ales Bartos, Libuse Noskova, Denisa Zimova, Michal Zido, Iva Hoffmanova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):37-43 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.033 
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system with a greater frequency in young adults. It has been speculated for some time, that an altered intestinal barrier is may be involved in the ethiopathogenesis of this disease, too. In our study we observed that the function of the intestinal epithelium can be impaired by increased permeability in patients with CIS and CDMS, however, no significant intestinal damage has been found. Based on the results CLDN-3 may play a role as potential biomarker of intestinal barrier disruption in patients with multiple sclerosis, mainly with treatment, but further contribution of CLDN3 from other compartments needs to be elucidated, e.g., the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier.
Number and dynamics of micronuclei and near-tetraploidy predict prognosis in childhood acute leukaemia
Sopiko Jashiashvili, Alla Zedginidze, Giorgi Ormotsadze, Asmat Shengelaia
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):44-48 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.046 
The aim of this investigation was to select markers of genetic instability and the genotoxicity of treatment for acute leukaemia, using the individual characteristics of patients to predict later complications. Eighty-six children with acute leukaemia were examined, on days 15 and 33, and the results were compared with clinical and laboratory data. The authors paid particular attention to the presence of polyploidy clones, where the modal number of chromosomes was associated with prognosis and dynamics of leukemic cells during the treatment and also focused on the level of micronuclei (Mn), one of the indicators of genetic instability. The authors examined Mn in buccal cavity cells since this is non-invasive and accessible.
Experimental model of primary intraocular lymphoma based on BALB/CaNn strain and A20 cells is optimal for investigational research
Eva Skrlova, Eva Uherkova, Aneta Klimova, Diana Malarikova, Petra Svozilkova, Petr Matous, Vit Herynek, Tomas Kucera, Pavel Klener, Jarmila Heissigerova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):49-55 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.003 
The purpose of this project was to compare the characteristics of two experimental murine models of primary intraocular lymphoma (PIOL) and determine which experimental model is most suitable for further investigational research. PIOL was induced in immunocompetent mice with intravitreal injection of syngeneic B-cell lymphoma cell lines. Murine strain C3H/HeN and cell line 38C13 were used in the first model and BALB/CaNn mice and cell line A20 were used in the second model. During the experiments, thorough clinical and histological evaluations were carried out. PIOL in BALB/CaNn mice was less aggressive with slower progression which predisposes this strain to be more suitable for further research.
Comparison of toric intraocular lens tilt and decentration measurement using dynamic Purkinje-meter and anterior segment optical coherence tomography
Eliska Palkovicova, Jiri Cendelin, Jiri Novak
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):56-65 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.017 
The correct position of the intraocular lens and its stability in the capsular bag is crucial for the quality of the retinal image after cataract or refractive surgery. Although some tilt and decentration of the intraocular lens are common, greater extent of the tilt and decentration cause optical aberrations which have a negative impact on patients' visual comfort. The purpose of the article was to describe a new dynamic Purkinje-meter, an experimental method for intraocular lens position measurement based on the analysis of Purkinje images which could have a wider use than the existing static Purkinje-meters. The method was verified on a group of pseudophakic eyes: the values of decentration and tilt measured on the dynamic Purkinje-meter were comparable to those from commercially available anterior segment optical coherence tomography CASIA2.
Study protocol - Prospective case-control trial - Impact of significant carotid stenosis on retinal perfusion measured with automated retinal oximetry
Petr Polidar, Barbora Paskova, Marta Karhanova, Martin Sin, Tomas Dornak, Zuzana Schreiberova, Petra Divisova, Tomas Veverka, David Franc, Daniel Sanak, Michal Kral
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):66-71 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.052 
The manuscript describes the protocol for a prospective study evaluating the relationship between carotid stenosis and retinal oxygen metabolism. Carotid stenosis is a major cause of ischaemic stroke worldwide. Retinal oximetry imaging of retinal blood vessels is noninvasive and capable of direct examination of the post-stenotic blood flow. It may be useful in differentiating high and low risk stenosis of the same severity. The results will yield more information about adaptive changes in the post-stenotic basin and may reveal mechanisms behind larger ischaemic deficits in some stroke patients. Previous studies have demonstrated that retinal blood flow is affected in a variety of eye and systemic diseases, including diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, and glaucoma.



