Biomedical papers, 2025 (vol. 169), issue 3
Reviews
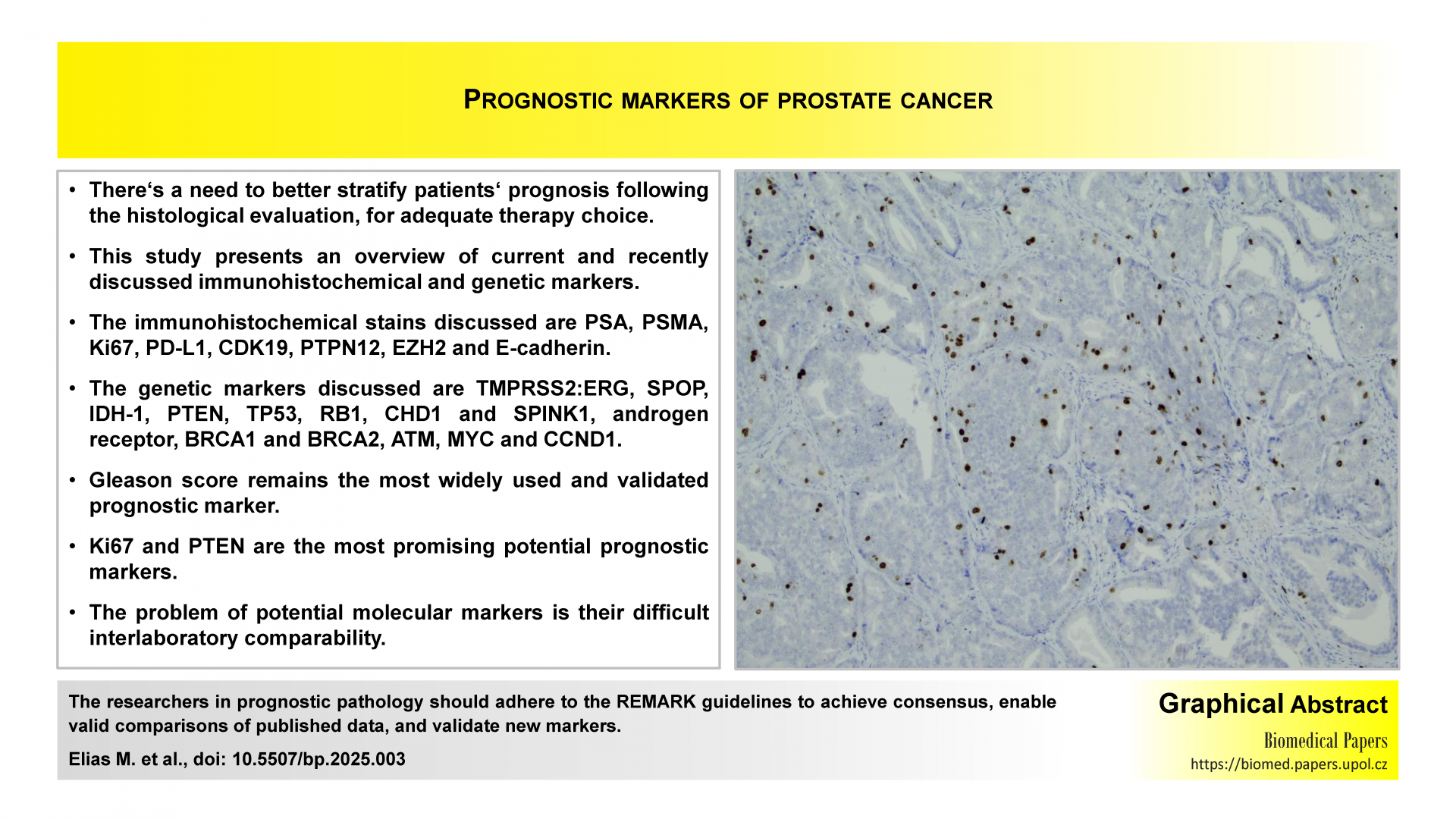
Contemporary review of prognostic markers of prostate cancer from a pathologist perspective
Martin Elias, Jan Bouchal, Milan Kral, Daniela Kurfurstova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):149-160 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.003 
There is a current need to better stratify patient prognosis following histological evaluation for prostate cancer in order to optimise therapy decisions. In this article, the authors provide an overview of some recently discussed putative prognostic markers. These include the immunohistochemical stains PSA, PSMA, Ki67, PD-L1, CDK19, PTPN12, EZH2 and E-cadherin and the genes TMPRSS2:ERG, SPOP, IDH-1, PTEN, TP53, RB1, CHD1 and SPINK1, the androgen receptor, BRCA1 and BRCA2, ATM, MYC and CCND1. The results are not easy to interpret due to wide variations in a number of key variables. Overall, the Gleason score is still the most widely used and most validated of the prognostic markers. Ki67 and PTEN are the most promising.
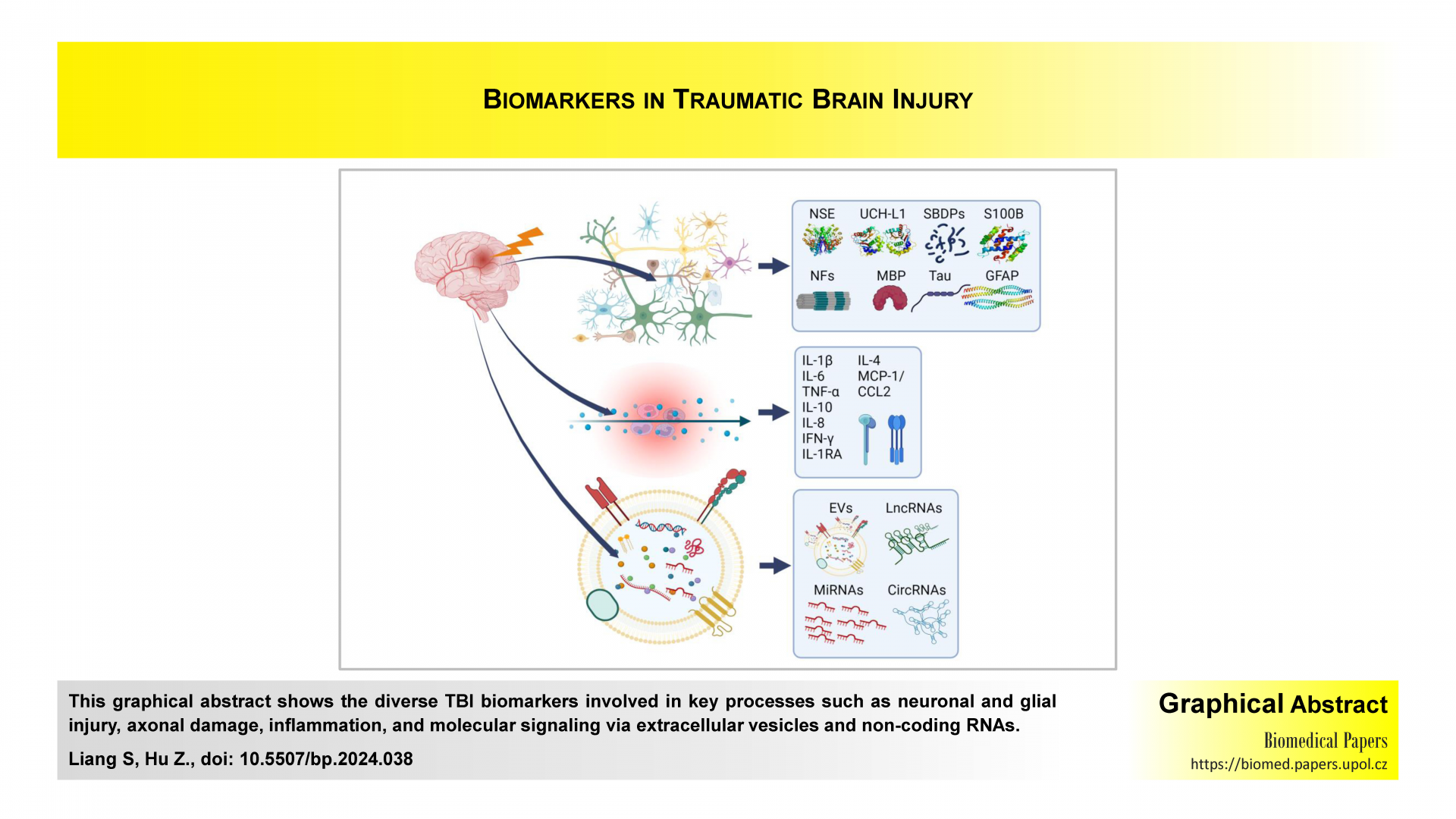
Unveiling the predictive power of biomarkers in traumatic brain injury: A narrative review focused on clinical outcomes
Sitao Liang, Zihui Hu
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):161-178 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.038 
This review explores novel insights into the use of biomarkers for traumatic brain injury (TBI) prognosis and management. By examining emerging evidence on neuronal injury, inflammation, extracellular vesicles and non-coding RNAs, it underscores their potential in predicting clinical outcomes such as recovery and cognitive impairment. The work bridges a critical gap between basic research and clinical application, offering a comprehensive perspective on advancing diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for TBI.
Original papers
Dysfibrinogenemia and hypofibrinogenemia - Spectrum of pathogenic variants in Slovak patients
Dominika Jaraskova, Jan Chandoga, Angelika Batorova, Tatiana Prigancova, Miriama Juhosova, Pavol Durina, Alzbeta Vavrova, Silvia Dallemule, Robert Petrovic, Anna Kyselova, Denisa Jankovicova, Daniel Bohmer
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):179-187 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.025 
Congenital hypofibrinogenemia (CH) and congenital dysfibrinogenemia (CD) are rare coagulation disorders caused by quantitative or qualitative defects in the fibrinogen gene. In this study, the authors, working to identify genetic variants and expanding knowledge about genetic variants in Slovak patients with congenital fibrinogen disorders registered at the National Haemophilia Centre. Molecular-genetic analysis have revealed six novel variants in 36 patients - FGA c.923_968dup p.(Gly324Lysfs*44) and FGG c.1105C>T p.(His369Tyr) were identified in CD patients. In CH patients, in the FGG gene c.8G>A p.(Trp3*), c.823G>T p.(Glu275*) and c.323C>A p.(Ala108Asp) variants were detected. In the FGB gene c.1427C>T p.(Ser476Leu) was identified.
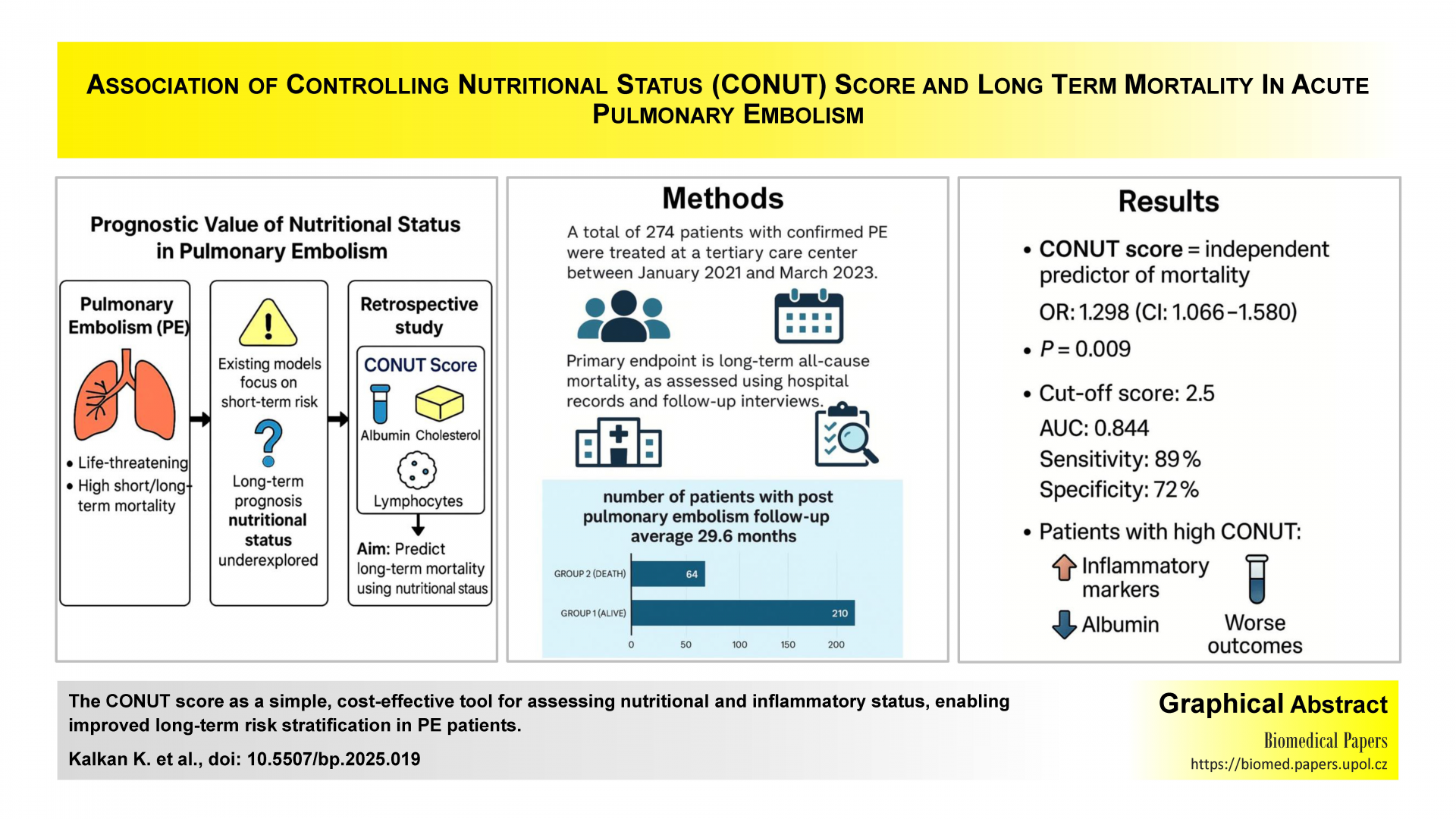
Association of controlling nutritional status score and long-term mortality in acute pulmonary embolism
Kamuran Kalkan, Cagatay Tunca, Veysel Ozan Tanik
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):188-195 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.019 
This study evaluates the prognostic relevance of the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score in long-term mortality among patients with pulmonary embolism (PE). By integrating serum albumin, total cholesterol, and lymphocyte count, the CONUT score provides a comprehensive assessment of nutritional and immunological status. The findings suggest that the CONUT score may offer valuable insights for long-term risk stratification in PE, complementing existing clinical and biomarker-based approaches.
Enhancing the utility of chromosome 6 and 8 testing in uveal melanoma biopsies
Veronika Matuskova, Pavla Hornackova, Marek Michalec, Lenka Zlamalikova, Kvetoslava Matulova, Michal Uher
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):196-202 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.018 
This article addresses the issue of chromosomal testing in patients with uveal melanoma. It is currently the only examination that can predict the development of metastases in patients with malignant uveal melanoma. The significance of chromosome 3 testing is unequivocal. This article deals with the testing of chromosomes 6 and 8 and their importance in predicting metastatic involvement. In a retrospective study, a cohort of 54 patients underwent testing of melanoma chromosome 6 and 8 from enucleated eyes. The authors demonstrated the importance of chromosome 8 abnormalities in patients without monosomy 3. The gain of chromosome 8, in fact, overturns the favourable prognosis of disomy 3. Currently, for the first time in the history of ophthalmology, a drug has been approved that extends survival in metastatic uveal melanoma. Chromosomal testing in samples of malignant melanoma is gaining significance.
Effect of treatment with carteolol and latanoprost in newly diagnosed primary open-angle glaucoma on peripapillary vessel density
Jan Lestak, Martin Fus, Sarka Pitrova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):203-209 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.010 
This work evaluates the effect of carteolol and latanoprost on vessel density in the peripapillary area of the optic nerve head. These drugs were chosen for two reasons: latanoprost is recommended by the European Glaucoma Society as the first-line drug for glaucoma. Carteolol works on a different principle but should not have any ischemic effect on the vascular system of the eye. In a previous study, during a 5-year follow-up of patients receiving beta-blockers (carteolol) and prostaglandins (latanoprost), the authors demonstrated a greater progression of visual field changes with prostaglandins than with beta-blockers. This led them, with the introduction of OCT angiography, to investigate whether they could detect changes in the vessels of the posterior pole of the eye in early-stage and newly diagnosed cases of primary open-angle glaucoma. The results showed that only patients treated with carteolol experienced a statistically significant improvement in vessel density.

Awareness and knowledge of diabetic retinopathy in diabetics and non-diabetics: A descriptive cross-sectional study
Diala Walid Abu-Hassan, Mona Freihat, Ibraheem Saleh, Iman Aolymat, Manar Zraikat, Muawyah Dawoud Al-Bdour
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):210-217 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.002 
A high awareness level of diabetic retinopathy was found among Jordanians but the knowledge level is only average. More focus on enhancing knowledge level of diabetic retinopathy should be a priority. With an increase in the educational level of Jordanians and other populations, awareness has increased though information/ education should be improved, particularly information from medical professionals. Enrichment of the social media and internet websites with evidence-based information about diseases by medical professionals may help in improving the situation. The authors assessed the knowledge of diabetic complications among unaffected individuals. This may assist in improving the general knowledge about DR and may also help in preventing diabetes.
Comparison of the efficacy of cisplatin and carboplatin in combination with etoposide in firstline treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in real-world practice in the Czech Republic - a retrospective analysis of patients from the LUCAS project
Alzbeta Bejckova, Miloslav Marel, Zdenka Chladkova, Libor Fila, Luis Fernando Casas-Mendez, Ondrej Venclicek, Petr Jakubec, Marketa Cernovska, Michal Hrnciarik, Jana Krejci, Petr Domecky, Martin Svaton
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):218-225 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.019 
The aim of this study was to determine whether there is a difference in the efficacy of palliative treatment depending on the use of cisplatin or carboplatin in combination with etoposide in patients with ES-SCLC in real-world practice in the Czech Republic. The authors performed a retrospective analysis of a cohort of 348 patients from the LUCAS project with ESSCLC. 79 patients were treated with etoposide plus cisplatin and 265 were treated with etoposide plus carboplatin. No statistically significant difference in mOS or mPFS was found depending on the use of carboplatin or cisplatin in combination with etoposide. In the subgroup analysis according to age and performance status (PS), no statistically significant difference in mOS was found either.
Surgical therapy in advanced sinonasal carcinomas - retrospective study
Lumír Hrabalek, Vlastimil Novak, Jiri Hoza, Csaba Hucko, Miroslav Vaverka, David Krahulik, Daniel Pohlodek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):226-231 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.020 
In this retrospective study, the authors assessed patients with an advanced sinonasal tumor treated with a surgical technique combining a frontal transbasal approach and endoscopic endonasal approach. The cohort consisted of ten patients. Complete resection (R0) was achieved in 8 cases (80%) and subcomplete resection in two (20%). In patients who died, the overall survival averaged 17.5 months (5-36 months). In surviving patients the average length of the follow up is 30.5 months (12-59). A combined endoscopic and transbasal approach presents an advantageous surgical strategy as it allows for greater radicality, reliable skull base reconstruction and reduces the need for extensive cranial approaches.
Case report
Schwannoma of the phrenic nerve. A case report
Josef Chudacek, Tomas Bohanes, Marek Szkorupa, Martin Stasek, Jan Hanuliak, Daniela Skanderova, Dusan Klos
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):232-234 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.011 
Neurogenic tumors are the third most common type of tumors in the mediastinum, often found in the posterior area but sometimes in the middle mediastinum. The case described involved a male with a middle mediastinum tumor, undiagnosable via biopsy due to its location. Surgery removed the tumor and phrenic nerve, confirming a low-activity schwannoma. Diagnosis of such tumors is challenging though surgical removal is viable for circumscribed tumors. Minimally invasive surgery is preferred, offering fewer complications and quick recovery.
This issue was published with support of Zentiva company




