Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):98-106 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.005
Two de novo UBR1 variants in trans as a cause of Johanson-Blizzard syndrome
- 1 Department of Medical Genetics, Faculty of Medicine in Pilsen, Charles University and University Hospital Pilsen, Pilsen, Czech Republic
- 2 Sikl's Department of Pathology, University Hospital Pilsen, Pilsen, Czech Republic
- 3 Biopticka laborator s.r.o., Pilsen, Czech Republic
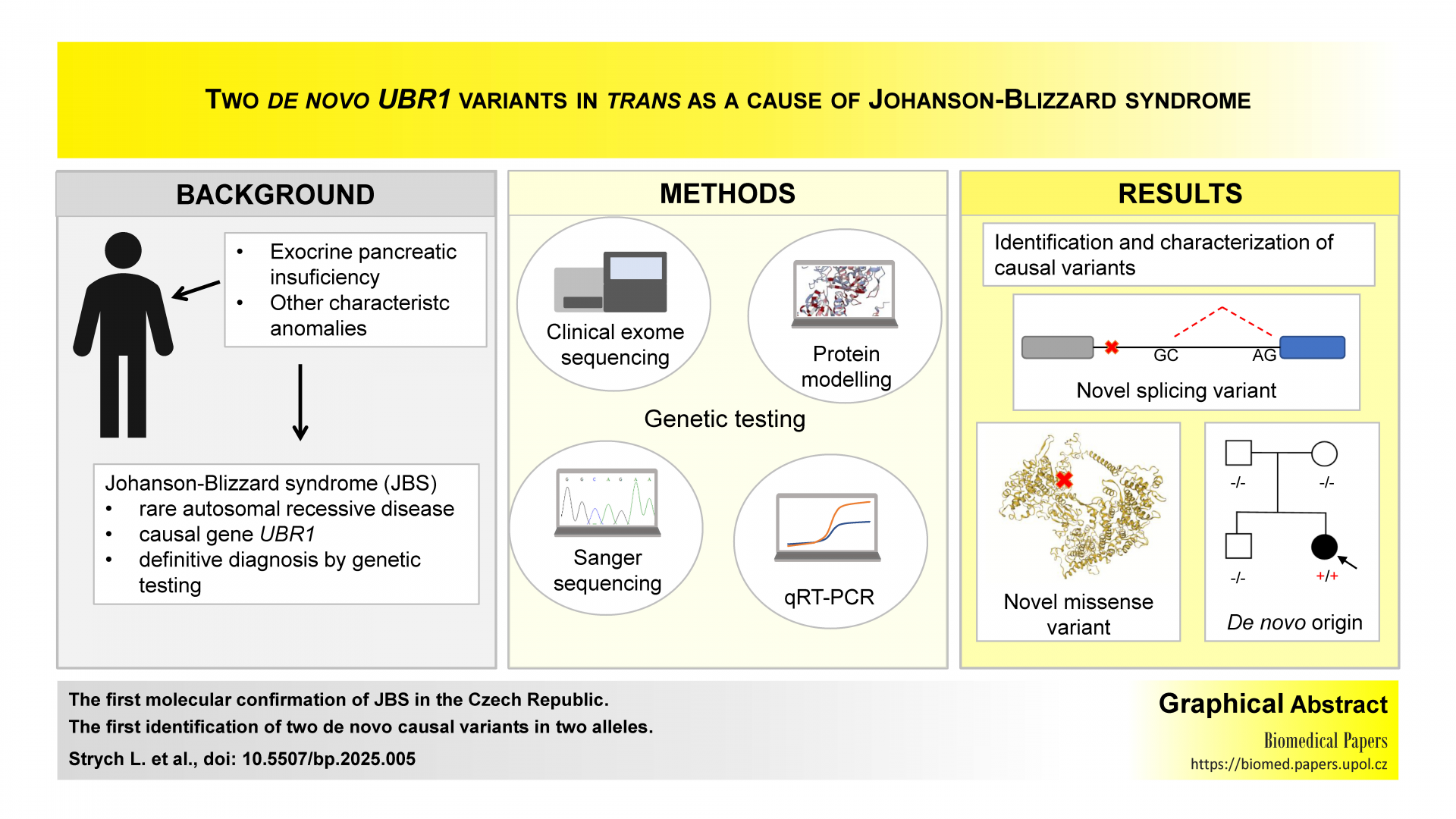
Aims/Background: Johanson-Blizzard syndrome (JBS) is a rare autosomal recessive disease caused by pathogenic variants in the UBR1 gene. JBS is usually suspected based on characteristic anomalies, but only genetic testing provides a definitive diagnosis. Since most variants are inherited from the parents, we aimed to identify the causal variants in a Czech proband with clinically suspected JBS and perform segregation analysis.
Methods: A proband with clinically suspected JBS underwent clinical exome sequencing (CES). Sanger sequencing was used for the validation, characterization, and segregation of variants in the family. The variants were also characterized using quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) and in silico analysis.
Results: Using CES in the proband, we identified two novel causal variants in the UBR1 gene, c.3482A>C and c.3509+6T>C. Although the variants were found in trans, neither was detected in the parents. Sanger sequencing of the cDNA revealed that the novel variant c.3509+6T>C caused activation of the non-canonical GC donor splice site. The inclusion of 70 bp of the intronic sequence generated a frameshift and a premature termination codon leading to nonsense-mediated decay, as detected by qPCR. In silico protein structural analysis showed that the novel missense variant c.3482A>C in the zinc-stabilized domain RING-H2 altered a highly conserved zinc-coordinating histidine by proline.
Conclusion: To the best of our knowledge, we report the first molecular confirmation of JBS in the Czech Republic and the first identification of two de novo causal variants in two alleles. Our findings also expand the spectrum of pathogenic variants in the UBR1 gene.
Keywords: Johanson-Blizzard syndrome, UBR1 gene, novel variant, de novo
Received: December 9, 2024; Revised: January 27, 2025; Accepted: January 28, 2025; Prepublished online: February 5, 2025; Published: June 1, 2025 Show citation
References
- . Sukalo M, Fiedler A, Guzmán C, Spranger S, Addor M-C, Mcheik JN, Oltra Benavent M, Cobben JM, Gillis LA, Shealy AG, Deshpande C, Bozorgmehr B, Everman DB, Stattin E-L, Liebelt J, Keller K-M, Bertola DR, van Karnebeek CDM, Bergmann C, Liu Z, Düker G, Rezaei N, Alkuraya FS, Oğur G, Alrajoudi A, Venegas-Vega CA, Verbeek NE, Richmond EJ, Kirbiyik Ö, Ranganath P, Singh A, Godbole K, Ali FAM, Alves C, Mayerle J, Lerch MM, Witt H, Zenker M. Mutations in the Human UBR1 Gene and the Associated Phenotypic Spectrum. Hum Mutat 2014;35(5):521-31.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Zenker M, Mayerle J, Lerch MM, Tagariello A, Zerres K, Durie PR, Beier M, Hülskamp G, Guzman C, Rehder H, Beemer FA, Hamel B, Vanlieferinghen P, Gershoni-Baruch R, Vieira MW, Dumic M, Auslender R, Gil-da-Silva-Lopes VL, Steinlicht S, Rauh M, Shalev SA, Thiel C, Winterpacht A, Kwon YT, Varshavsky A, Reis A. Deficiency of UBR1, a ubiquitin ligase of the N-end rule pathway, causes pancreatic dysfunction, malformations and mental retardation (Johanson-Blizzard syndrome). Nat Genet 2005;37(12):1345-50.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Johanson A, Blizzard R. A syndrome of congenital aplasia of the alae nasi, deafness, hypothyroidism, dwarfism, absent permanent teeth, and malabsorption. J Pediatr 1971;79(6):982-7.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Varshavsky A. N-degron and C-degron pathways of protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2019;116(2):358-66.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Bartel B, Wünning I, Varshavsky A. The recognition component of the N-end rule pathway. EMBO J 1990;9(10):3179-89.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Tasaki T, Mulder LCF, Iwamatsu A, Lee MJ, Davydov I V., Varshavsky A, Muesing M, Kwon YT. A Family of Mammalian E3 Ubiquitin Ligases That Contain the UBR Box Motif and Recognize N-Degrons. Mol Cell Biol 2005;25(16):7120-36.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Varshavsky A. The N-end rule: functions, mysteries, uses. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1996;93(22):12142-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Kwon YT, Reiss Y, Fried VA, Hershko A, Yoon JK, Gonda DK, Sangan P, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Varshavsky A. The mouse and human genes encoding the recognition component of the N-end rule pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 1998;95(14):7898-903.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Tasaki T, Zakrzewska A, Dudgeon DD, Jiang Y, Lazo JS, Kwon YT. The Substrate Recognition Domains of the N-end Rule Pathway. J Biol Chem 2009;284(3):1884-95.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Xie Y. The E2-E3 interaction in the N-end rule pathway: the RING-H2 finger of E3 is required for the synthesis of multiubiquitin chain. EMBO J 1999;18(23):6832-44.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Du F, Navarro-Garcia F, Xia Z, Tasaki T, Varshavsky A. Pairs of dipeptides synergistically activate the binding of substrate by ubiquitin ligase through dissociation of its autoinhibitory domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci 2002;99(22):14110-15.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Pan M, Zheng Q, Wang T, Liang L, Mao J, Zuo C, Ding R, Ai H, Xie Y, Si D, Yu Y, Liu L, Zhao M. Structural insights into Ubr1-mediated N-degron polyubiquitination. Nature 2021;600(7888):334-8.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Hwang C-S, Sukalo M, Batygin O, Addor M-C, Brunner H, Aytes AP, Mayerle J, Song HK, Varshavsky A, Zenker M. Ubiquitin Ligases of the N-End Rule Pathway: Assessment of Mutations in UBR1 That Cause the Johanson-Blizzard Syndrome. PLoS One 2011;6(9):e24925.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Sukalo M, Mayerle J, Zenker M. Clinical utility gene card for: Johanson-Blizzard syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 2014;22(1):152.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Gonzaga-Jauregui C, Lupski J. Genomics of rare diseases : understanding rare disease genetics through genomic approaches. Amsterdam: Academic Press; 2021.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 2012;9(4):357-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, Durbin R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009;25(16):2078-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Quinlan AR, Hall IM. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010;26(6):841-2.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med 2015;17(5):405-24.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L, Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS, Sunyaev SR. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat Methods 2010;7(4):248-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Cheng J, Novati G, Pan J, Bycroft C, ®emgulytė A, Applebaum T, Pritzel A, Wong LH, Zielinski M, Sargeant T, Schneider RG, Senior AW, Jumper J, Hassabis D, Kohli P, Avsec ®. Accurate proteome-wide missense variant effect prediction with AlphaMissense. Science 2023;381(6664):eadg7492. doi: 10.1126/science.adg7492
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Steinhaus R, Proft S, Schuelke M, Cooper DN, Schwarz JM, Seelow D. MutationTaster2021. Nucleic Acids Res 2021;49(W1):W446-W451.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Pejaver V, Urresti J, Lugo-Martinez J, Pagel KA, Lin GN, Nam H-J, Mort M, Cooper DN, Sebat J, Iakoucheva LM, Mooney SD, Radivojac P. Inferring the molecular and phenotypic impact of amino acid variants with MutPred2. Nat Commun 2020;11(1):5918.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Quang D, Chen Y, Xie X. DANN: a deep learning approach for annotating the pathogenicity of genetic variants. Bioinformatics 2015;31(5):761-3.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Kumar P, Henikoff S, Ng PC. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc 2009;4(7):1073-81.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Gough J, Karplus K, Hughey R, Chothia C. Assignment of homology to genome sequences using a library of hidden Markov models that represent all proteins of known structure. J Mol Biol 2001;313(4):903-19.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Jaganathan K, Kyriazopoulou Panagiotopoulou S, McRae JF, Darbandi SF, Knowles D, Li YI, Kosmicki JA, Arbelaez J, Cui W, Schwartz GB, Chow ED, Kanterakis E, Gao H, Kia A, Batzoglou S, Sanders SJ, Farh KK-H. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019;176(3):535-548.e24.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Zeng T, Li YI. Predicting RNA splicing from DNA sequence using Pangolin. Genome Biol 2022;23(1):103.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Jian X, Boerwinkle E, Liu X. In silico prediction of splice-altering single nucleotide variants in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res 2014;42(22):13534-44.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Stenson PD, Mort M, Ball E V., Chapman M, Evans K, Azevedo L, Hayden M, Heywood S, Millar DS, Phillips AD, Cooper DN. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD®): optimizing its use in a clinical diagnostic or research setting. Hum Genet 2020;139(10):1197-207.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Riley GR, Jang W, Rubinstein WS, Church DM, Maglott DR. ClinVar: public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Res 2014;42(D1):D980-D985.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Fokkema IFAC, Taschner PEM, Schaafsma GCP, Celli J, Laros JFJ, den Dunnen JT. LOVD v.2.0: the next generation in gene variant databases. Hum Mutat 2011;32(5):557-63.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Thorvaldsdottir H, Robinson JT, Mesirov JP. Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV): high-performance genomics data visualization and exploration. Brief Bioinform 2013;14(2):178-92.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Strych L, Černá M, Hejnalová M, Zavoral T, Komrsková P, Tejcová J, Bitar I, Sládková E, Sýkora J, ©ubrt I. Targeted long-read sequencing identified a causal structural variant in X-linked nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. BMC Med Genomics 2024;17(1):29.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . ©imková H, Faltus V, Marvan R, Pexa T, Stenzl V, Brouček J, Hořínek A, Mazura I, Zvárová J. Allele frequency data for 17 short tandem repeats in a Czech population sample. Forensic Sci Int Genet 2009;4(1):e15-e17.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R, Schwede T. SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 2018;46(W1):W296-W303.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Sehnal D, Bittrich S, Deshpande M, Svobodová R, Berka K, Bazgier V, Velankar S, Burley SK, Koča J, Rose AS. Mol* Viewer: modern web app for 3D visualization and analysis of large biomolecular structures. Nucleic Acids Res 2021;49(W1):W431-W437.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Nagy E, Maquat LE. A rule for termination-codon position within intron-containing genes: when nonsense affects RNA abundance. Trends Biochem Sci 1998;23(6):198-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Zhu W, Li J, Chen S, Zhang J, Vetrini F, Braxton A, Eng CM, Yang Y, Xia F, Keller KL, Okinaka-Hu L, Lee C, Holder JL, Bi W. Two de novo novel mutations in one SHANK3 allele in a patient with autism and moderate intellectual disability. Am J Med Genet Part A 2018;176(4):973-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Wang M, Kishnani P, Decker-Phillips M, Kahler SG, Chen YT, Godfrey M. Double mutant fibrillin-1 (FBN1) allele in a patient with neonatal Marfan syndrome. J Med Genet 1996;33(9):760-3.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Tessitore A, Sinisi AA, Pasquali D, Cardone M, Vitale D, Bellastella A, Colantuoni V. A Novel Case of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2A Associated with Two de Novo Mutations of the RETProtooncogene*. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1999;84(10):3522-7.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Salipante SJ, Benson KF, Luty J, Hadavi V, Kariminejad R, Kariminejad MH, Rezaei N, Horwitz MS. Double de novo mutations ofELA2 in cyclic and severe congenital neutropenia. Hum Mutat 2007;28(9):874-81.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Mongan NP, Jääskeläinen J, Green K, Schwabe JW, Shimura N, Dattani M, Hughes IA. Two de Novo Mutations in the AR Gene Cause the Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome in a Pair of Monozygotic Twins. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2002;87(3):1057-61.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Debeer P, Huysmans C, Van de Ven WJM, Fryns J, Devriendt K. Carpal and tarsal synostoses and transverse reduction defects of the toes in two brothers heterozygous for a double de novo NOGGIN mutation. Am J Med Genet Part A 2005;134A(3):318-20.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . Lundén L, Boxhammer S, Carlsson G, Ellström K, Nordenskjöld M, Lagerstedt-Robinson K, Fadeel B. Double de novo mutations of ELANE ( ELA2 ) in a patient with severe congenital neutropenia requiring high-dose G-CSF therapy. Br J Haematol 2009;147(4):587-90.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Stella A, Lastella P, Viggiano L, Bagnulo R, Resta N. Clinical presentation and genetic analyses of neurofibromatosis type 1 in independent patients with monoallelic double de novo closely spaced mutations in the NF1 gene. Hum Mutat 2022;43(10):1354-60.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Bernkopf M, Abdullah UB, Bush SJ, Wood KA, Ghaffari S, Giannoulatou E, Koelling N, Maher GJ, Thibaut LM, Williams J, Blair EM, Kelly FB, Bloss A, Burkitt-Wright E, Canham N, Deng AT, Dixit A, Eason J, Elmslie F, Gardham A, Hay E, Holder M, Homfray T, Hurst JA, Johnson D, Jones WD, Kini U, Kivuva E, Kumar A, Lees MM, Leitch HG, Morton JE V., Németh AH, Ramachandrappa S, Saunders K, Shears DJ, Side L, Splitt M, Stewart A, Stewart H, Suri M, Clouston P, Davies RW, Wilkie AOM, Goriely A. Personalized recurrence risk assessment following the birth of a child with a pathogenic de novo mutation. Nat Commun 2023;14(1):853.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Sheth N, Roca X, Hastings ML, Roeder T, Krainer AR, Sachidanandam R. Comprehensive splice-site analysis using comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 2006;34(14):3955-67.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source... - . REESE MG, EECKMAN FH, KULP D, HAUSSLER D. Improved Splice Site Detection in Genie. J Comput Biol 1997;4(3):311-23.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Ghosh R, Harrison SM, Rehm HL, Plon SE, Biesecker LG. Updated recommendation for the benign stand-alone ACMG/AMP criterion. Hum Mutat 2018;39(11):1525-30.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Pertesi M, Vallée M, Wei X, Revuelta M V., Galia P, Demangel D, Oliver J, Foll M, Chen S, Perrial E, Garderet L, Corre J, Leleu X, Boyle EM, Decaux O, Rodon P, Kolb B, Slama B, Mineur P, Voog E, Le Bris C, Fontan J, Maigre M, Beaumont M, Azais I, Sobol H, Vignon M, Royer B, Perrot A, Fuzibet J-G, Dorvaux V, Anglaret B, Cony-Makhoul P, Berthou C, Desquesnes F, Pegourie B, Leyvraz S, Mosser L, Frenkiel N, Augeul-Meunier K, Leduc I, Leyronnas C, Voillat L, Casassus P, Mathiot C, Cheron N, Paubelle E, Moreau P, Bignon Y, Joly B, Bourquard P, Caillot D, Naman H, Rigaudeau S, Marit G, Macro M, Lambrecht I, Cliquennois M, Vincent L, Helias P, Avet-Loiseau H, Moreno V, Reis RM, Varkonyi J, Kruszewski M, Vangsted AJ, Jurczyszyn A, Zaucha JM, Sainz J, Krawczyk-Kulis M, W±tek M, Pelosini M, Iskierka-Jażdżewska E, Grz±¶ko N, Martinez-Lopez J, Jerez A, Campa D, Buda G, Lesueur F, Dudziński M, García-Sanz R, Nagler A, Rymko M, Jamroziak K, Butrym A, Canzian F, Obazee O, Nilsson B, Klein RJ, Lipkin SM, McKay JD, Dumontet C. Exome sequencing identifies germline variants in DIS3 in familial multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2019;33(9):2324-30.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Khan K, Mehmood S, Liu C, Siddiqui M, Ahmad A, Faiz BY, Chioza BA, Baple EA, Ullah MI, Akram Z, Satti HS, Khan R, Harlalka GV, Jameel M, Akram T, Baig SM, Crosby AH, Hassan MJ, Zhang F, Davis EE, Khan TN. A recurrent rare intronic variant in CAPN3 alters mRNA splicing and causes autosomal recessive limb-girdle muscular dystrophy-1 in three Pakistani pedigrees. Am J Med Genet A 2022;188(2):498-508. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62545
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Garcia-Barcena C, Osinalde N, Ramirez J, Mayor U. How to Inactivate Human Ubiquitin E3 Ligases by Mutation. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020;8:39. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00039
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Chen A, Wu K, Fuchs SY, Tan P, Gomez C, Pan ZQ. The Conserved RING-H2 Finger of ROC1 Is Required for Ubiquitin Ligation. J Biol Chem 2000;275(20):15432-9.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed... - . Caswell RC, Gunning AC, Owens MM, Ellard S, Wright CF. Assessing the clinical utility of protein structural analysis in genomic variant classification: experiences from a diagnostic laboratory. Genome Med 2022;14(1):77.
 Go to original source...
Go to original source...  Go to PubMed...
Go to PubMed...
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0), which permits use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original publication is properly cited. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.




