Biomedical papers - Latest articles
Results 31 to 60 of 89:
Comparison of toric intraocular lens tilt and decentration measurement using dynamic Purkinje-meter and anterior segment optical coherence tomographyOriginal papers
Eliska Palkovicova, Jiri Cendelin, Jiri Novak
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):56-65 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.017 
The correct position of the intraocular lens and its stability in the capsular bag is crucial for the quality of the retinal image after cataract or refractive surgery. Although some tilt and decentration of the intraocular lens are common, greater extent of the tilt and decentration cause optical aberrations which have a negative impact on patients' visual comfort. The purpose of the article was to describe a new dynamic Purkinje-meter, an experimental method for intraocular lens position measurement based on the analysis of Purkinje images which could have a wider use than the existing static Purkinje-meters. The method was verified on a group of pseudophakic eyes: the values of decentration and tilt measured on the dynamic Purkinje-meter were comparable to those from commercially available anterior segment optical coherence tomography CASIA2.
Experimental model of primary intraocular lymphoma based on BALB/CaNn strain and A20 cells is optimal for investigational researchOriginal papers
Eva Skrlova, Eva Uherkova, Aneta Klimova, Diana Malarikova, Petra Svozilkova, Petr Matous, Vit Herynek, Tomas Kucera, Pavel Klener, Jarmila Heissigerova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):49-55 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.003 
The purpose of this project was to compare the characteristics of two experimental murine models of primary intraocular lymphoma (PIOL) and determine which experimental model is most suitable for further investigational research. PIOL was induced in immunocompetent mice with intravitreal injection of syngeneic B-cell lymphoma cell lines. Murine strain C3H/HeN and cell line 38C13 were used in the first model and BALB/CaNn mice and cell line A20 were used in the second model. During the experiments, thorough clinical and histological evaluations were carried out. PIOL in BALB/CaNn mice was less aggressive with slower progression which predisposes this strain to be more suitable for further research.
Number and dynamics of micronuclei and near-tetraploidy predict prognosis in childhood acute leukaemiaOriginal papers
Sopiko Jashiashvili, Alla Zedginidze, Giorgi Ormotsadze, Asmat Shengelaia
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):44-48 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.046 
The aim of this investigation was to select markers of genetic instability and the genotoxicity of treatment for acute leukaemia, using the individual characteristics of patients to predict later complications. Eighty-six children with acute leukaemia were examined, on days 15 and 33, and the results were compared with clinical and laboratory data. The authors paid particular attention to the presence of polyploidy clones, where the modal number of chromosomes was associated with prognosis and dynamics of leukemic cells during the treatment and also focused on the level of micronuclei (Mn), one of the indicators of genetic instability. The authors examined Mn in buccal cavity cells since this is non-invasive and accessible.
Impaired intestinal permeability in patients with multiple sclerosisOriginal papers
Lenka Fialova, Pavla Barilly, Ivana Stetkarova, Ales Bartos, Libuse Noskova, Denisa Zimova, Michal Zido, Iva Hoffmanova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):37-43 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.033 
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system with a greater frequency in young adults. It has been speculated for some time, that an altered intestinal barrier is may be involved in the ethiopathogenesis of this disease, too. In our study we observed that the function of the intestinal epithelium can be impaired by increased permeability in patients with CIS and CDMS, however, no significant intestinal damage has been found. Based on the results CLDN-3 may play a role as potential biomarker of intestinal barrier disruption in patients with multiple sclerosis, mainly with treatment, but further contribution of CLDN3 from other compartments needs to be elucidated, e.g., the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier.
Results of surgical therapy of functioning pituitary adenomasOriginal papers
Vlastimil Novak, Lumir Hrabalek, Jan Schovanek, Zdenek Frysak, Racheal Temitope Ijisesan Perryova, Daniel Pohlodek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):32-36 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.037 
This study evaluates the results of surgical transnasal procedures in patients with functioning pituitary adenomas. The cohort consisted of 58 patients. Microadenoma was diagnosed in 58.6% and macroadenoma in 41.4%. In the group with excessive production of ACTH, complete remission was achieved after the first surgery in 78.6% of cases; in the group with excessive GH production in 51.4%. In the group with excessive production of PRL, it was 57.1%. Surgical therapy in the cohort described led to the normalisation of excessive hormone production in 58.6% of cases.
Clinical and molecular genetic analysis of cytologically uncertain thyroid nodules in patients with thyroid diseaseOriginal papers
Jindrich Lukas, Barbora Hintnausova, Vlasta Sykorova, Martin Syrucek, Marek Maly, David Lukas, Jaroslava Duskova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):26-31 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.048 
The study aimed to determine the preoperative clinical and molecular genetic risks of malignancy in indeterminate nodules (Bethesda III and IV) and their influence on the surgical treatment strategy of hemi/total thyroidectomy. Molecular tests were focused on the occurrence of pathogenic variants of somatic genes BRAF, RAS, TERT and rearrangements of RET/PTC, PAX8/PPARγ associated with thyroid oncogenesis. The incidence of clinical risk factors for malignancy was evaluated. The presence of at least one of these led to a significantly higher incidence of malignancy than in cases of their absence. From the experience of the authors so far, molecular genetic testing is one of the many decision-making factors in elective surgical procedures.
Percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung lesions is a safe method associated with a very low risk of pleural recurrenceOriginal papers
Martin Svaton, David Havel, Marcela Buresova, Jan Baxa, Petr Hosek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):21-25 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.030 
Percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung lesions is an alternative to bronchoscopic confirmation of lung lesions. The aim of this study was to assess the risk of pleural recurrence for all types of lung lesions. To the best of their knowledge, this has so far only been investigated in stage I lung tumors and not in all lung lesions. Secondary objectives included assessment of diagnostic yield and safety with respect to the incidence of pneumothorax and hemorrhage. In this study, percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of lung lesions showed high sensitivity and low degree of acute complications requiring an invasive solution. The risk of pleural recurrence after a biopsy was very low.
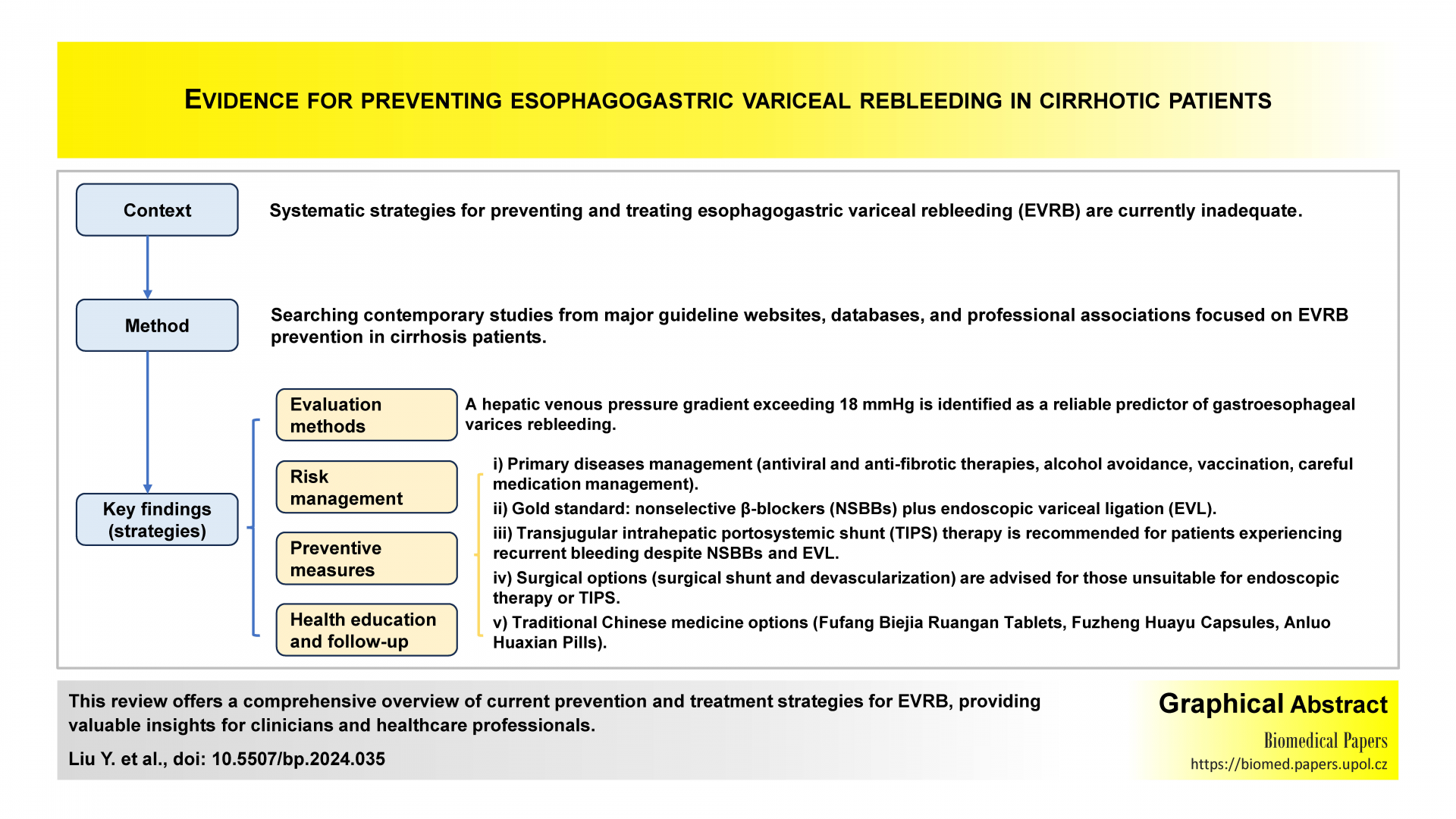
Evidence for preventing EVRB in cirrhotic patients: A systematic reviewReviews
Ye Liu, Xiaoyan Wang, Yingjia Gu, Dan Niu
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):9-20 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.035 
The authors included publications up to July 1, 2023. Five guidelines, 1 systematic review, and 2 expert consensuses were included. Twenty-four of the best levels were summarized. The evidence includes evaluation methods, risk management, preventive measures, health education and follow-up. This systematic review summarizes the latest evidence of the best level of EVRB prevention in liver cirrhosis. These are practical and can be used as reference for clinical and medical personnel.

Acute kidney injury due to gentamicin nephrotoxicity and specific miRNAs as biomarkersReviews
Viktor Klementa, Nadezda Petejova, Pavel Horak, Ester Kurasova, Josef Zadrazil
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):1-8 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.031 
Acute kidney injury induced by gentamicin nephrotoxicity is a significant clinical concern due to the widespread use of gentamicin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic. Gentamicin can cause damage to renal tubular cells, leading to decreased kidney function. Emerging research highlights the role of specific microRNAs (miRNAs) as potential biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. These miRNAs are small, non-coding RNA molecules involved in regulating gene expression, and their altered levels in the blood or urine can indicate kidney damage before traditional markers, such as serum creatinine. Identifying these miRNAs could improve diagnosis, enable timely intervention, and potentially mitigate the adverse effects of gentamicin on renal health.
Postcovid Guillain-Barré syndrome with severe course - case series two patients including clinical evaluation of smell and examination of olfactory event-related potentials (OERPs)Case report
Nikola Pastorkova, Karla Janouskova, Libor Vasina, Helene Schulz, Jaromir Astl, Richard Holy
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):354-358 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.014 
This work presents case reports of two patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with previous COVID19 that both patients survived. The sense of smell was investigated subjectively using sniffin' stick tests and objectively using objective olfactometry by the evaluation of olfactory event-related potentials (OERPs). Despite the severe course of post-covid GBS, no olfactory disturbance was detected. Both patients had good results on the smell tests. OERPs were plentiful in both cases.
Life expectancy in glioblastoma patients who had undergone stereotactic biopsy: a retrospective single-center studyOriginal papers
Matej Halaj, Ondrej Kalita, Lucie Tuckova, Lumir Hrabalek, Martin Dolezel, Jana Vrbkova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):349-353 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.030 
Progress in the of diagnostic and neurosurgical techniques of the last decade have enabled even safe resection of suspected GBMs located in eloquent brain regions. Currently, patients indicated for only the needle biopsy represent a minority group with a common poor prognosis. The purpose of stereotactic biopsy is to obviate misdiagnosis and to choose the optimal treatment strategy. The aim of this paper is to evaluate life expectancy in patients with GBM confirmed by needle biopsy and the relationship with the following oncotherapy. Patients in this study who had undergone oncotherapy, had a slight increase in overall survival. The effect of this treatment was enhanced in patients with favourable clinical factors such as age and Karnofsky score.
Occult fractures detected on radiographs in young children with a concern for abusive head traumaOriginal papers
Eliska Popelova, Zuzana Holubova, Marcela Dvorakova, Martin Kyncl
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):342-348 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.018 
Identifying infants and toddlers with abusive head trauma is challenging. Finding any evidence of trauma in these children is therefore very important. Dedicated skeletal radiographs of the whole skeleton should be performed in all children younger than two years evaluated for possible abuse. Our study showed that dedicated skeletal radiographs were only performed in 62% of children younger than two years evaluated for suspected abusive head trauma. Clinically occult fractures were revealed in 31% of these children. Moreover, the majority of these fractures had high specificity for abuse. Attention should be paid to increasing awareness of child abuse imaging protocols.
The association between preterm births and assisted reproductive technologiesOriginal papers
Anna Stastna, Eva Waldaufova, Tomas Fait
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):332-341 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.039 
While assisted reproductive technology (ART) offers hope to millions of couples worldwide in overcoming infertility, it also attracts attention to investigating the health outcomes of mothers and their children. Using Cox regression models, this study compares preterm birth risk between ART-assisted singleton pregnancies (in-vitro fertilisation (IVF) with fresh embryo transfer, frozen embryo transfer (FET) and oocyte receipt (OoR)) with non-ART singleton pregnancies. The results show a higher preterm birth risk in ART-treated women (1.56 to 2.06 depending on the ART method) compared to women without ART treatment. However, no statistically significant differences were found in the risk of preterm birth among ART-treated mothers based on specific ART methods.
Fetal magnetic resonance imaging in the confirmation of congenital anomalies found on routine mid-trimester ultrasoundOriginal papers
Ishraq Dhaifalah, Marek Godava, Jana Havalova, Pavla Hanzlikova, Kamila Michalkova, Lenka Bakaj Zbrozkova, Jakub Civrny, Howard Cuckle
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):326-331 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.008 
Most pregnant women are offered a routine ultrasound scan during the second trimester of pregnancy in order to detect fetal anomalies. In some cases, an anomaly suspected by ultrasound requires referral for a fetal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) examination in order to clarify the diagnosis. In this study a large series of such referrals was assessed, accounting for one in six women with a fetal anomaly on ultrasound. In general, the MRI findings supported the scan results but this varied according to the type of anomaly. This concordance was very high for anomalies of the urinary tract and face.
Gamma-glutamyltransferase-associated glycoprotein patterns in human seminal plasma of normozoospermic men: a new aspect of biomarker heterogeneityOriginal papers
Tamara Jankovic, Jelena Danilovic Lukovic, Sanja Goc, Ninoslav Mitic, Ljiljana Hajdukovic, Miroslava Jankovic
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):319-325 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.031 
Gamma-glutamyltransferase (GGT) is implicated in a variety of diseases, but it is not extensively studied in relation to reproductive physiology. An increase in GGT activity is associated with alterations in a specific fractional pattern of distinct molecular mass forms. In this study, seminal GGT forms were estimated and, for the first time, annotated with underlying patterns of sialylated and mannosylated glycoproteins. The GGT-associated glycoprotein patterns were established as an adjunct reference parameter to differentiate between known GGT molecular mass forms. These emerge as new targets for evaluation of its biomarker potential.
The renoprotective effect of Tibolone in sepsis-induced acute kidney injuryOriginal papers
Ejder Saylav Bora, Duygu Burcu Arda, Oytun Erbas
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):311-318 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.016 
This study breaks new ground by investigating Tibolone’s potential as a therapeutic agent in sepsis-induced acute kidney injury (AKI), an area largely unexplored previously. By delving into Tibolone’s effects on biomarkers like SIRT1 and YAP, as well as its impact on inflammatory and oxidative processes, it sheds light on its promising role in mitigating renal damage. The findings underscore Tibolone’s potential as a novel intervention for sepsis-associated AKI, urging further research for translational application in clinical settings.
Comparison of dose length product and image quality of a biphasic whole-body polytrauma CT protocol with and without the automatic tube voltage selectionOriginal papers
David Girsa, Karin Kremenova, Jiri Lukavsky, Lucie Sukupova, Hana Malikova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):304-310 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.004 
This work has shown that in terms of reducing the radiation load of the two-phase whole-body CT protocol used in the examination of polytraumatic patients, there is no difference whether we use only the function of automatic current modulation on the X-ray tube, or its combination with the function of automatic voltage selection. In the case of a combination of both functions, the image quality drops slightly. Significantly more important for the radiation load is the position of the patient's arms during the examination: if the arms are in the scanned volume along the body, the radiation load is significantly higher in both examined groups.
Safety and efficacy of simple training protocol in patients after mild traumatic brain injuryOriginal papers
Martina Martinikova, Robert Ruzinak, Petra Hnilicova, Michal Bittsansky, Marian Grendar, Lucia Babalova, Pavol Skacik, Ema Kantorova, Vladimir Nosal, Monika Turcanova Koprusakova, Jozef Sivak, Jana Sivakova, Zuzana Biringerova, Branislav Kolarovszki, Kamil Zelenak, Egon Kurca, Stefan Sivak
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):295-303 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.013 
In this paper, the authors show that simple physical and cognitive training after mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) can be positive for the brain and its functions and help in the prevention of post-concussion syndrome. This can lead to the decreased economic burden of mTBI, and individual training can be performed without professional supervision.
S100B protein as a biomarker and predictor in traumatic brain injuryOriginal papers
Stefan Trnka, Premysl Stejskal, Jakub Jablonsky, David Krahulik, Daniel Pohlodek, Lumir Hrabalek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):288-294 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.025 
Despite the known value of using S100B protein for its prognostic potential in cases of traumatic brain injury, the findings of this study are that the correlations between selected internal diseases, body habitus, season and S100B protein are not confirmed in TBI patients. Conversely, when interpreting the results of patients with polytrauma, it is important to remember that the S100B protein value is modified in this instance. A benefit that cannot be overlooked is that the S100B values are associated with good patient prognosis, offering therapeutic advantages in addition to the prognostic ones.
Acute pancreatitis as a risk factor of chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. An overviewReviews
David Solil, Petr Dite, Michal Senkyrik, Martina Bojkova, Bohuslav Kianicka
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):284-287 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.023 
Early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer and successful treatment is difficult. The optimization strategy is linked to identifying the specific subgroups of pancreatitis. To improve prognosis, it is crucial to identify patients at risk, in other words patients following acute pancreatitis and those with recurrent acute pancreatitis. The risk for pancreatic cancer development is very high in patients who are positive for other risk factors such as obesity, metabolic syndrome, alcohol abuse, smoking etc.
Exploring the benefits and challenges of AI-driven large language models in gastroenterology: Think out of the boxReviews
Jan Kral, Michal Hradis, Marek Buzga, Lumir Kunovsky
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(4):277-283 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.027 
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved significantly from its early concepts in the 1950s to today's advanced large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. This technology has the potential to revolutionize gastroenterology, including diagnosis, treatment, education, and decision-making support. The benefits to gastroenterology include accelerating diagnosis and treatment, providing personalized care, enhancing education, aiding decision-making, and improving patient communication. However, challenges like limited AI capability, biased data, errors, security and privacy concerns, and costs must be addressed. The future of LLMs in gastroenterology depends on processing large quantities of data, identifying patterns, and assisting in personalized treatment plans. Collaboration between AI developers, healthcare professionals, and regulatory bodies is essential for responsible use, ensuring LLMs support doctors and contribute to better patient care.
A severe case of pemphigoid gestationis persisting after labour - case report and review of the literatureCase report
Hynek Herman, Petr Krepelka, Adela T. Faridova, Klara Trojanova, Jiri Hanacek, Barbora Jaluvkova, Jaroslav Feyereisl, Spyridon Gkalpakiotis
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):271-275 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.010 
The communication on pemphigoid gestationis is of paramount importance not only because of the need to report such a serious disease in a professional journal, but also as a recommendation for possible treatment of this rare condition in pregnancy which a large number physicians and especially obstetricians may not encounter in their entire careers. As with other diseases, early and accurate diagnosis and subsequent early therapy is of primary importance, to obviate major deterioration in the condition, the risk to the pregnant woman and the fetus, and to the newborn after delivery.
The Czech National MS Registry (ReMuS): Data trends in multiple sclerosis patients whose first disease-modifying therapies were initiated from 2013 to 2021Original papers
Dominika Stastna, Jiri Drahota, Michal Lauer, Aneta Mazouchova, Ingrid Menkyova, Jana Adamkova, Radek Ampapa, Michal Dufek, Marketa Grunermelova, Pavel Hradilek, Eva Kubala Havrdova, Jan Mares, Alena Martinkova, Zbysek Pavelek, Marek Peterka, Eva Recmanova, Petra Rockova, Ivana Stetkarova, Pavel Stourac, Marta Vachova, Dana Horakova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):262-270 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.015 
Multiple sclerosis treatment strategies are changing in the Czech Republic. According to data from 2013-2021, the proportion of patients starting high-efficacy disease-modifying therapies is increasing. These findings come from the Czech National Multiple Sclerosis Registry ReMuS which provides a quality source of data for not only scientific publications, but national regulatory authorities as well. Its outputs offer feedback and a means for improving the management of multiple sclerosis in the future.
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) in acute hospitalized older patients focused on hydrationOriginal papers
Vladimir Hrabovsky, Martina Skrobankova, Zdenek Lys, Adela Vrtkova, Veronika Spacilova, Jan Vaclavik
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):256-261 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.038 
Ultrasound examination is non-invasive, simple to perform and it provides valuable information on a patient´s condition, including geriatric. Patients as older individuals frequently suffer from dehydration. This study showed that ultrasound assessment provides immediate key information for comprehensive understanding of clinical status in older patients and can be beneficial for optimizing the treatment strategy, including fluid management decisions.
Changes in vascular density in the macula after pars plana vitrectomy for idiopathic macular hole with macular peeling and one type of flapOriginal papers
Anna Tarkova, Nada Jiraskova, Jaroslava Dusova, Jan Marak, Jan Studnicka
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):248-255 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.017 
In this study, the authors focused on changes in the vascular density of the superficial and deep vascular plexus in temporal and foveal-sparing flap after pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) with macular peel. The vascular density of the deep plexus increased in both groups and the vascular density of the superficial plexus was almost the same in the temporal flap and in the foveal-sparing flap was reduced during the one-year follow-up period. The results were also confirmed by the anatomical improvement. The authors demonstrated a statistical relationship between the duration of symptoms and changes in the microvasculature in the macula in both groups. No significant differences were found between the various forms of the flap method used in PPV.
A stylet use may be beneficial for elective and rescue intubation of prematurely born infants < 30 weeksOriginal papers
Klara Dunajova, Tereza Lamberska, Truong An Nguyen, Adam Kubica, Petr Kudrna, Richard Plavka
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):243-247 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.015 
This study challenges the prevailing view that stylet use during intubation offers no benefit, specifically in the context of premature infants in the delivery room. Through the detailed analysis of 104 intubation attempts across 70 infants, the authors found that employing a stylet significantly enhances the success rate of initial intubation attempts, shortens the procedure's duration, and lowers the risk of severe desaturation events. The evidence suggests that the use of a stylet could be significant for stabilization of extremely premature infants during the golden hour of their life, marking a significant shift in current practices for this vulnerable population.
Severe congenital T-lymphocytopenia may affect the outcome of neonatal intensive careOriginal papers
Ivana Hulinkova, Veronika Medova, Andrea Soltysova, Veronika Dobsinska, Andrej Ficek, Peter Ciznar
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):235-242 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.028 
This study evaluated the amount of TREC in a group of risk newborns and found a significant association between low TREC values and the occurrence of sepsis. The authors identified an association between mortality in preterm neonates with sepsis in patients with TREC < 5th percentile and they hypothesize that low TREC values may be a surrogate marker for mortality in preterm neonates.
A comparison of heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction in the Moravian Midlands Registry with the LCZ696 patients in the Paradigm-HF trialOriginal papers
Ludek Pavlu, Marek Vicha, Jakub Flasik, Jana Petrkova, Milos Taborsky, Tereza Kacirkova, Ondrej Holy
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):229-234 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.006 
This study aspired to provide comprehensive real-world data on a population with heart failure in the Moravian region of the Czech Republic. The authors compared local clinically relevant data with those from the ground-breaking Paradigm-HF trial and they found that local patients had a more advanced state of heart failure. The high prevalence of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICD) and cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) confirms access to advanced and financially demanding treatment options in this region.
Influence of graft anastomosis and graft morphology on long-term patency of the saphenous vein after aortocoronary bypassOriginal papers
Okaikor Okantey, Tomas Jonszta, Jiri Sieja, Miriam Kende, Radim Brat, Lubomir Pavliska
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):223-228 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.013 
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is a surgical modality that resolves ischemic myocardial disease. The success of the procedure depends on a number of factors. Construction of the anastomosis and graft characteristics play a functional role in graft patency. This follow-up analysis of a study on the effects of endoscopic vein harvest after bypass surgery compared the outcome of sequential anastomoses and single grafts, vein graft length and diameter, calcium score, and target artery quality on long-term vein graft patency. The differences between sequential and individual grafts were not statistically significant. Graft and target artery diameters had a statistically significant influence on patency. Longer graft lengths and higher calcium scores were associated with statistically significant graft occlusion.
Ultrasonographic signs as predictors of metastatic involvement in the axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer patients: from minimal changes to the appearance of the pathological lymph node. A retrospective analysisOriginal papers
Lucia Veverkova, Marketa Koleckova, Katherine Vomackova, Nora Zlamalova, Lubica Lowova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2024, 168(3):216-222 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.009 
This is a retrospective analysis of ultrasound findings in axillary lymph nodes in the patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer. The study focuses on the minimal morphological changes as early signs of metastatic involvement. This could be the basis for the design of a scoring system to evaluate axillary lymph nodes apropos sonographic features and with regard to the type of primary breast cancer and its aggressiveness. This retrospective evaluation and research may contribute to better ultrasound evaluation of lymph nodes in breast cancer patients



