Biomedical papers - Latest articles
Results 1 to 30 of 89:
Primary ventriculitis caused by Streptococcus intermedius - a rare case and challenge with uncertain clinical outcome. Case reportCase report
Stefan Trnka, Premysl Stejskal, Jakub Jablonsky, David Krahulik, Eva Cechakova, Lumir Hrabalek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):298-300 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.029 
This case report presents a unique instance of primary ventriculitis in a 53-year-old patient with no predisposing factors, caused by the rare pathogen Streptococcus intermedius. Despite early and targeted antibiotic therapy, the patient's condition did not improve, highlighting the challenges in managing such infections. Imaging studies and cerebrospinal fluid analysis were crucial for diagnosis, revealing significant inflammation and ventricular debris. This case emphasizes the need for further research into the treatment of primary ventriculitis, as standard therapeutic approaches may not always be effective. The findings underscore the importance of early detection and the complexity of managing central nervous system infections.
Urinary tract trauma as a predictor of acute kidney injury in severely injured patients: A retrospective analysis of observational studiesOriginal papers
Michal Frelich, Jan Pavlicek, Filip Bursa, Vojtech Vodicka, Dana Salounova, Peter Sklienka
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):293-297 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.026 
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of the most common organ dysfunctions in major trauma. Patients with multiple injuries are exposed to several risk factors for AKI, including haemorrhage, systemic inflammation, rhabdomyolysis, and secondary insults from emergency surgery and infection. Because the development of AKI is associated with multiple adverse outcomes, such as increased length of hospital stay, mortality, and total cost of healthcare, it is essential to identify all risk factors early and, in indicated cases, initiate preventive measures with the aim of reducing the incidence of AKI and subsequent complications. Although it seems intuitive that direct injury to the urinary tract would affect its function, very little is known about the risk of AKI in this setting. In this study, the authors demonstrated that injury to the urinary tract was an independent predictor of the development of AKI with an RR of 3.4 (95% CI 2.25-5.06), whereas injury to the kidneys or their vascular supply resulted in a threefold increased risk of AKI (RR = 3.1, 95% CI 1.93-4.90), and injury to the urinary passages had an RR of 4.2 (95% CI 2.70-6.46). Based on AUC ROC curve analysis, the authors found that NGAL levels measured within 24 h of admission were a reliable predictor of AKI only in patients without urinary tract injury.
The role of Fetuin-A and Leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein in the diagnosis of prostate cancer - a pilot studyOriginal papers
Alena Sorokac Kubolkova, Gabriel Varga, Miroslava Benovska, Lenka Kovacova, Michal Fedorko
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):288-292 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.028 
In recent years, several studies have been conducted to develop different biomarkers of prostate cancer with high sensitivity and specificity. Minimal studies have so far focused on Fetuin-A and Leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein (LRG1) as potential biomarkers for prostate cancer. This article reports on these 2 potential biomarkers, that have been investigated in their department and can help in future screening for early detection and diagnosis, reduce the number of unnecessary biopsies, assess the risk of aggressive disease, and monitor response to prostate cancer treatment. Through this study, Fetuin-A has proven to be a potential new biomarker for prostate cancer.
Comparison of myocardial perfusion study and invasive hemodynamic measurement of the significance of non-infarct-related residual stenoses in ST elevation myocardial infarction patientsOriginal papers
Jan Vacha, Miloslav Spacek, Milan Kaminek, Martin Hutyra, Radomir Nykl, Martin Sluka, Milos Taborsky
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):281-287 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.021 
The authors present the results of their study focused on patients with acute STEMI and multivessel coronary artery disease. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) guided staged intervention of the so far silent non-IRA lesions (50-90%) was performed 4-8 weeks after STEMI closely preceded by myocardial perfusion study (MPS). We offer a comparative analysis of these methods within real-world scenarios. The major finding was that they observed weak correlation in ischemia detection between MPS using SPECT and invasive hemodynamic measurement using FFR. In patients with abnormal myocardium detected by MPS significantly lower FFR values were observed in the non-IRAs compared to patients with negative MPS studies. Further studies are needed to guide the optimal treatment strategy in such patients.
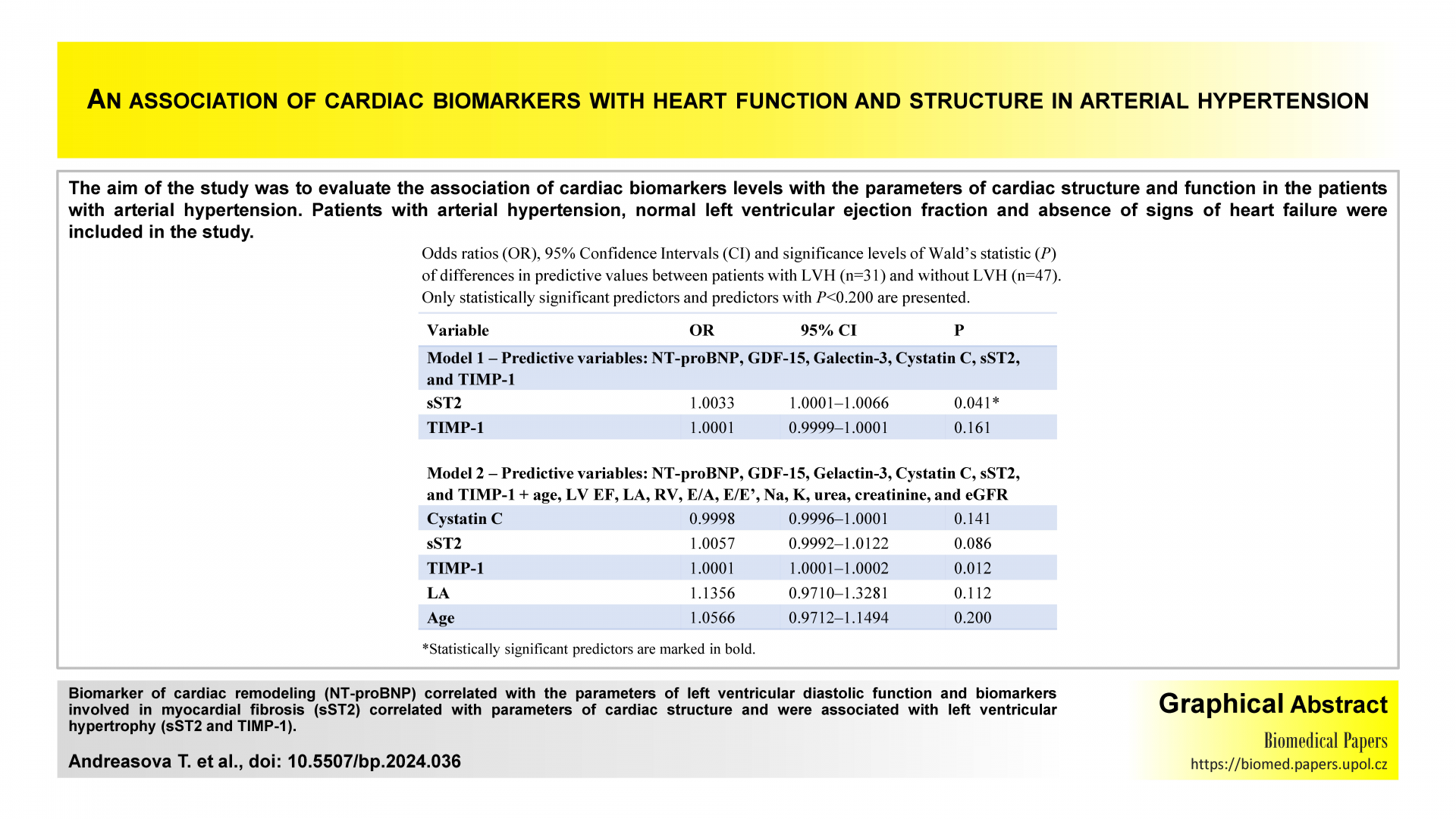
Association of biomarkers of cardiac remodeling, myocardial fibrosis and inflammation with parameters of heart function and structure in patients with arterial hypertensionOriginal papers
Tana Andreasova, Filip Malek, Zuzana Jiraskova Zakostelska, Petr Neuzil, Jana Vranova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):272-280 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.036 
The aim of the study was to evaluate the association of cardiac biomarkers levels with the parameters of cardiac structure and function in the patients with arterial hypertension. Patients with arterial hypertension, normal left ventricular ejection fraction and absence of signs of heart failure were included in the study. Biomarker of cardiac remodeling (NT-proBNP) correlated with the parameters of left ventricular diastolic function and biomarkers involved in myocardial fibrosis (sST2) correlated with parameters of cardiac structure and were associated with left ventricular hypertrophy (sST2 and TIMP-1).
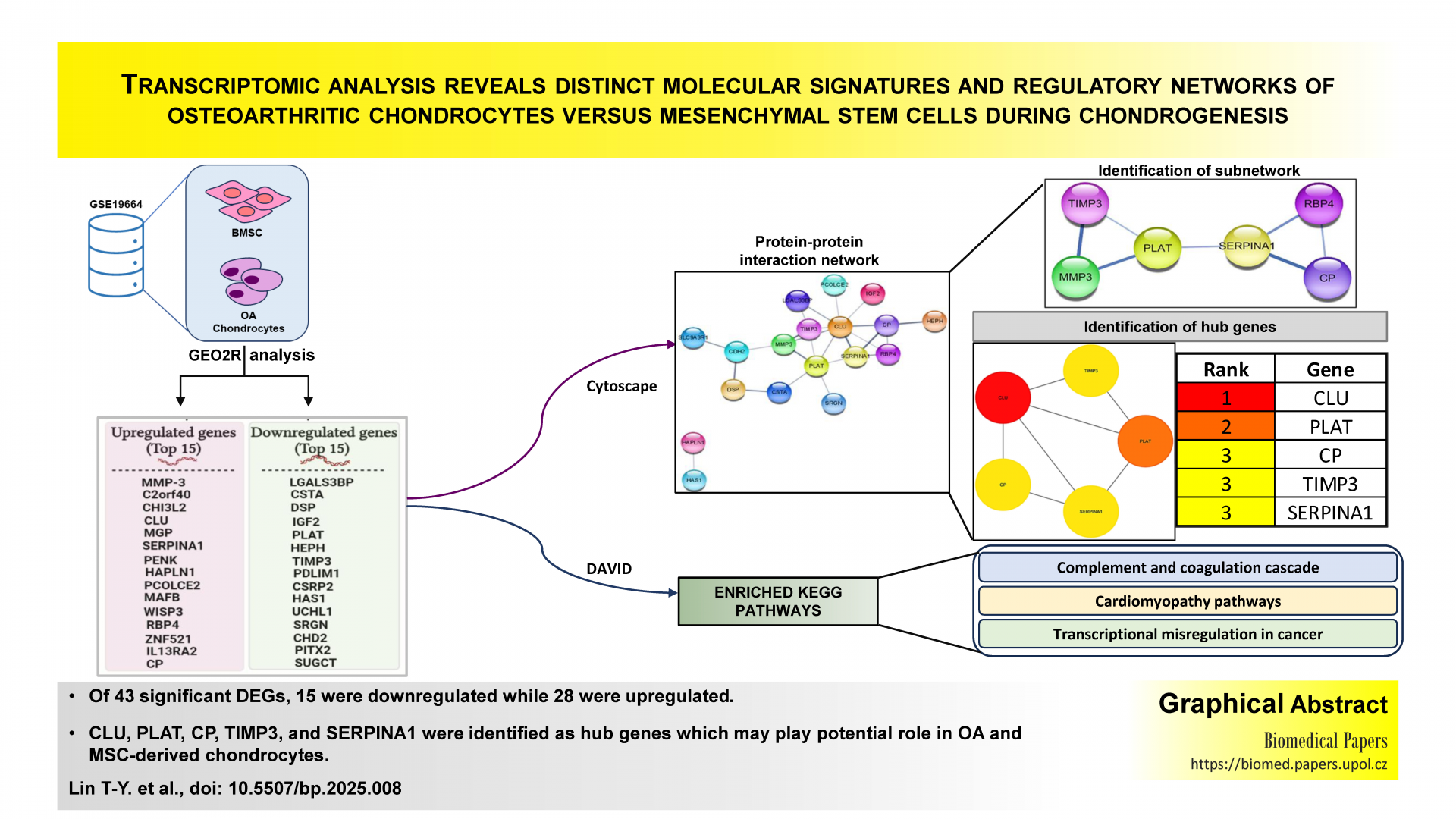
Transcriptomic analysis reveals distinct molecular signatures and regulatory networks of osteoarthritic chondrocytes versus mesenchymal stem cells during chondrogenesisOriginal papers
Tsung-Yu Lin, Viraj Krishna Mishra, Rajni Dubey, Thakur Prasad Chaturvedi, Shankar Narayan A, Hsu-Wei Fang, Lung-Wen Tsai, Navneet Kumar Dubey
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):262-271 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.008 
This bioinformatics study aimed to determine differentially expressed genes (DEGs) patterns of knee osteoarthritis chondrocytes versus human bone marrow stem cells towards chondrogenic commitment. We identified 43 DEGs (15 downregulated and 28 upregulated) and enriched pathways, which revealed the enrichment of complement and coagulation cascades and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy pathways for upregulated and downregulated DEGs, respectively. Hub networks identified the top 5 hub genes, including CLU, PLAT, CP, TIMP3, and SERPINA1.
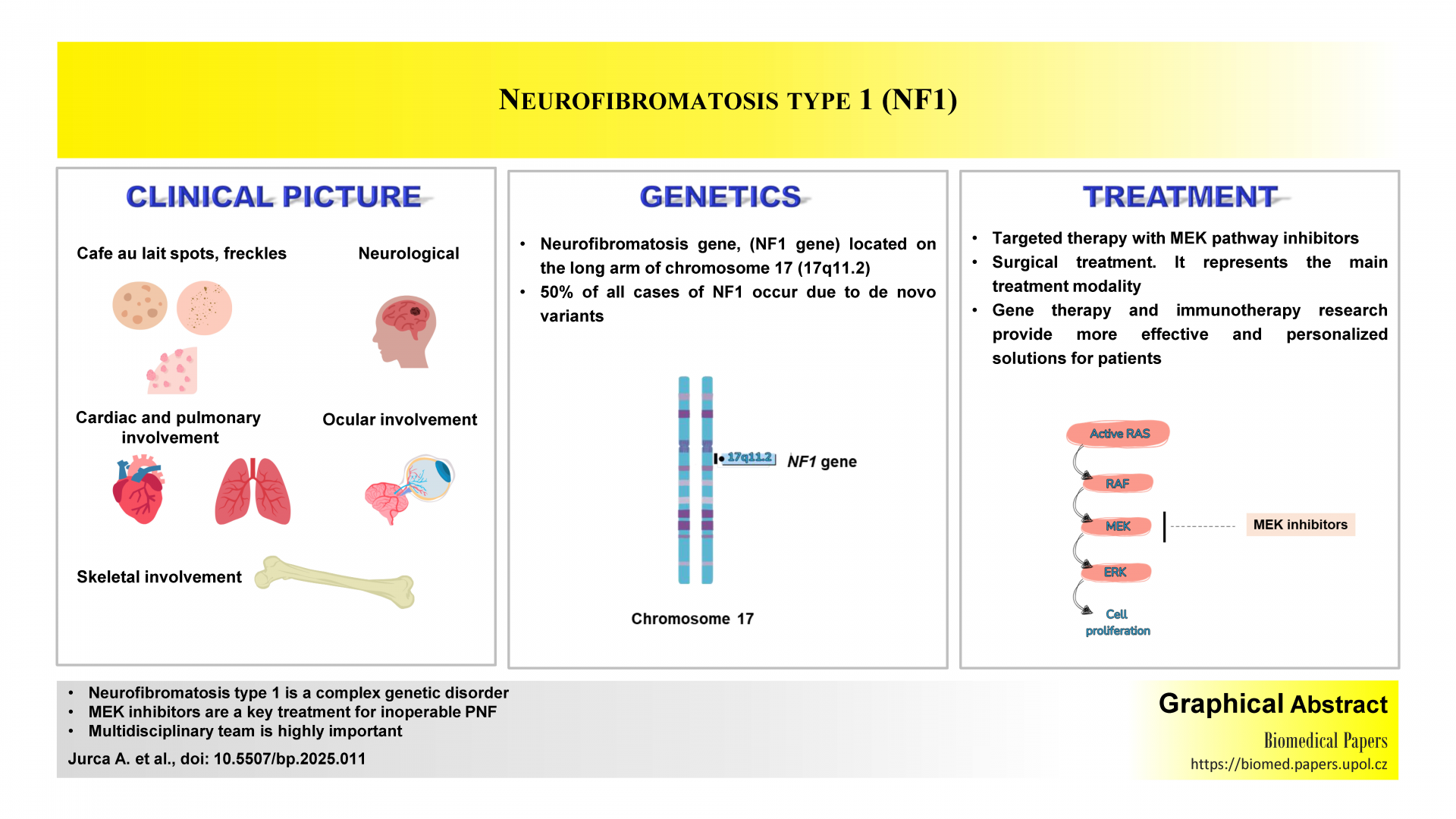
Unveiling the complexity of neurofibromatosis type 1: Innovations in genetic understanding and clinical management. A narrative reviewReviews
Aurora Jurca, Simona Pop, Claudia Maria Jurca, Cosmin Mihai Vesa, Alexandru Daniel Jurca
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):255-261 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.011 
This narrative review offers a unique perspective on recent advances in the genetics, diagnosis, and management of neurofibromatosis type 1. Unlike previous studies, it incorporates the updated 2021 NIH criteria, emphasizing the role of genetic testing for early diagnosis and personalized treatment. The article highlights genotype-phenotype correlations, the impact of specific mutations on disease severity, and the need for continuous monitoring. It also covers less commonly addressed aspects, such as the increased breast cancer risk in women with NF1, emerging therapies like MEK inhibitors, and the importance of tailored surveillance, making it a valuable contribution to NF1 management.
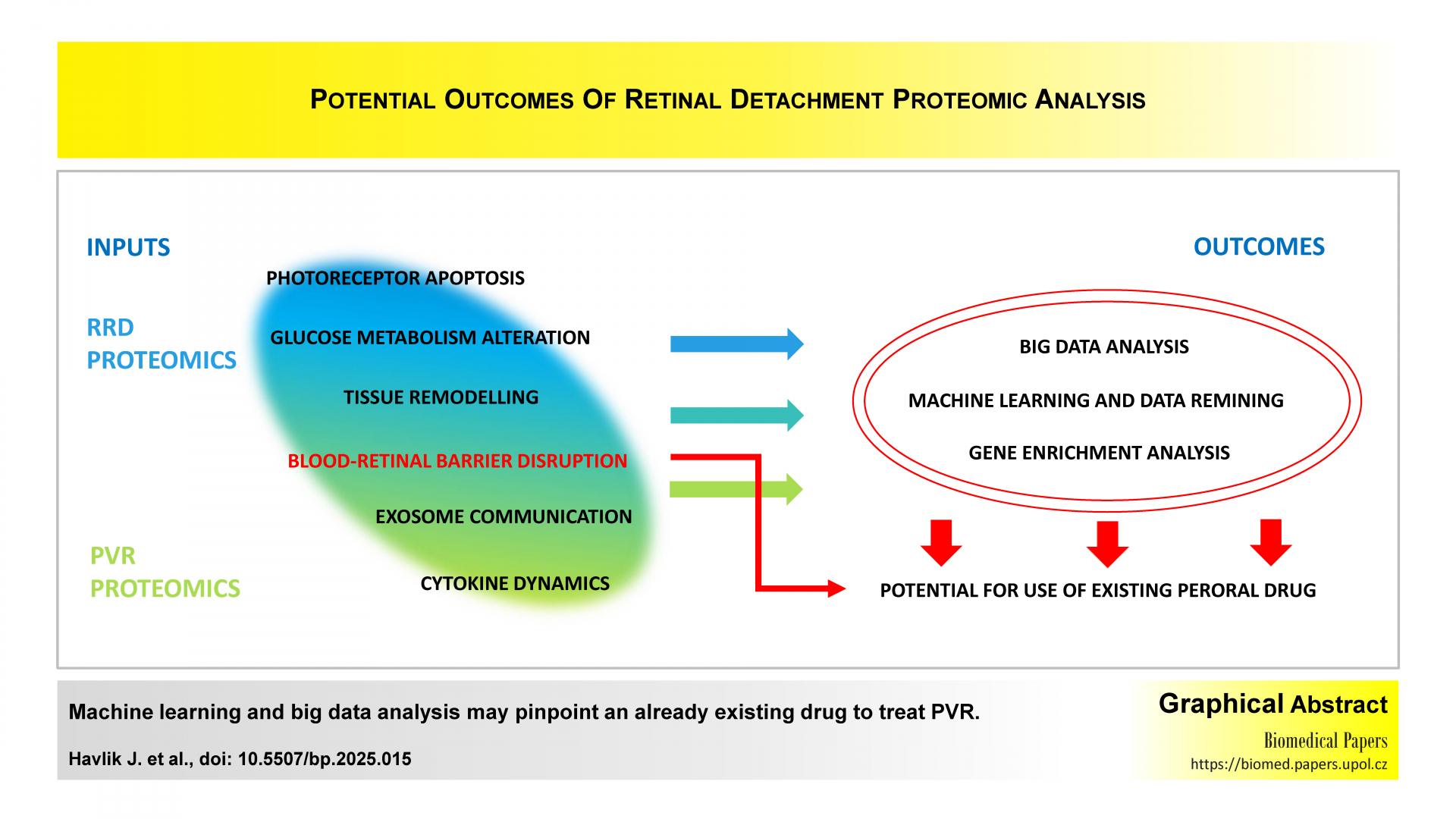
Vitreous proteomics in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment and proliferative vitreoretinopathyReviews
Jan Havlik, Martin Lada, Jan Tesar, Vladimir Kratky, Martin Sin
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):247-254 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.015 
Proteomic analysis of the vitreous has unveiled critical molecular mechanisms underlying retinal pathologies, highlighting novel therapeutic opportunities. This study explores the dynamic protein changes associated with detachment-induced photoreceptor degeneration, metabolic stress, and inflammation. Key findings reveal altered glycolytic enzymes, antioxidant depletion, and cytokine dysregulation, underscoring their roles in cellular damage and repair. The review emphasizes the transformative potential of advanced proteomics, such as data-independent acquisition and exosome profiling, in identifying biomarkers and therapeutic targets, paving the way for precision medicine in combating vision-threatening conditions.
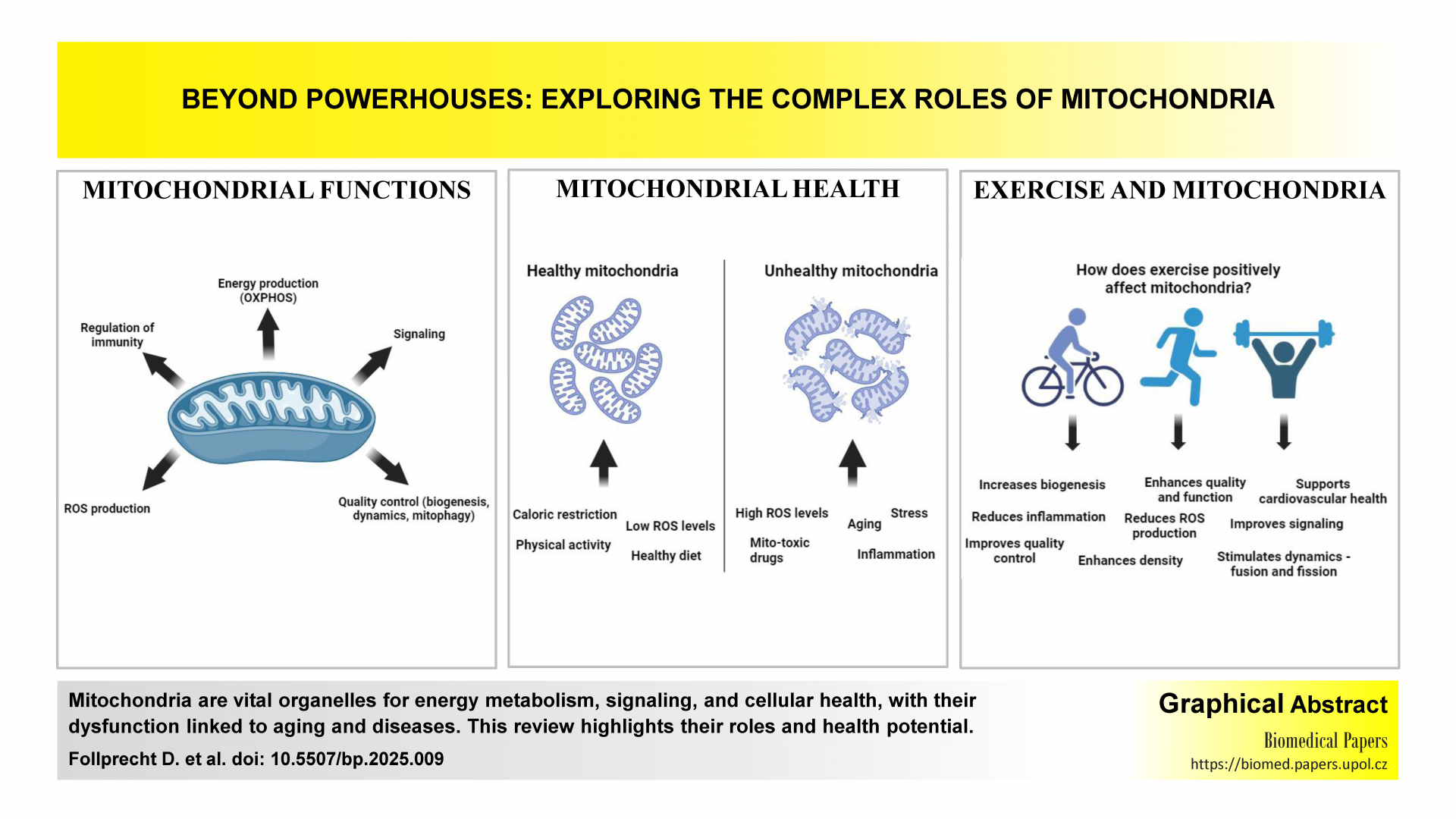
Mitochondria in focus: From structure and function to their role in human diseases. A reviewReviews
Daniel Follprecht, Jakub Vavricka, Viktorie Johankova, Pavel Broz, Ales Krouzecky
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):235-246 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.009 
This work provides an in-depth exploration of mitochondrial functions beyond energy production, highlighting their essential roles in cellular processes, signaling, and health maintenance. By emphasizing recent advances in mitochondrial research, the manuscript underscores the impact of mitochondria in aging, disease, and exercise, offering valuable insights that could guide therapeutic strategies for enhancing mitochondrial health and longevity
Schwannoma of the phrenic nerve. A case reportCase report
Josef Chudacek, Tomas Bohanes, Marek Szkorupa, Martin Stasek, Jan Hanuliak, Daniela Skanderova, Dusan Klos
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):232-234 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.011 
Neurogenic tumors are the third most common type of tumors in the mediastinum, often found in the posterior area but sometimes in the middle mediastinum. The case described involved a male with a middle mediastinum tumor, undiagnosable via biopsy due to its location. Surgery removed the tumor and phrenic nerve, confirming a low-activity schwannoma. Diagnosis of such tumors is challenging though surgical removal is viable for circumscribed tumors. Minimally invasive surgery is preferred, offering fewer complications and quick recovery.
Surgical therapy in advanced sinonasal carcinomas - retrospective studyOriginal papers
Lumír Hrabalek, Vlastimil Novak, Jiri Hoza, Csaba Hucko, Miroslav Vaverka, David Krahulik, Daniel Pohlodek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):226-231 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.020 
In this retrospective study, the authors assessed patients with an advanced sinonasal tumor treated with a surgical technique combining a frontal transbasal approach and endoscopic endonasal approach. The cohort consisted of ten patients. Complete resection (R0) was achieved in 8 cases (80%) and subcomplete resection in two (20%). In patients who died, the overall survival averaged 17.5 months (5-36 months). In surviving patients the average length of the follow up is 30.5 months (12-59). A combined endoscopic and transbasal approach presents an advantageous surgical strategy as it allows for greater radicality, reliable skull base reconstruction and reduces the need for extensive cranial approaches.
Comparison of the efficacy of cisplatin and carboplatin in combination with etoposide in firstline treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer in real-world practice in the Czech Republic - a retrospective analysis of patients from the LUCAS projectOriginal papers
Alzbeta Bejckova, Miloslav Marel, Zdenka Chladkova, Libor Fila, Luis Fernando Casas-Mendez, Ondrej Venclicek, Petr Jakubec, Marketa Cernovska, Michal Hrnciarik, Jana Krejci, Petr Domecky, Martin Svaton
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):218-225 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.019 
The aim of this study was to determine whether there is a difference in the efficacy of palliative treatment depending on the use of cisplatin or carboplatin in combination with etoposide in patients with ES-SCLC in real-world practice in the Czech Republic. The authors performed a retrospective analysis of a cohort of 348 patients from the LUCAS project with ESSCLC. 79 patients were treated with etoposide plus cisplatin and 265 were treated with etoposide plus carboplatin. No statistically significant difference in mOS or mPFS was found depending on the use of carboplatin or cisplatin in combination with etoposide. In the subgroup analysis according to age and performance status (PS), no statistically significant difference in mOS was found either.

Awareness and knowledge of diabetic retinopathy in diabetics and non-diabetics: A descriptive cross-sectional studyOriginal papers
Diala Walid Abu-Hassan, Mona Freihat, Ibraheem Saleh, Iman Aolymat, Manar Zraikat, Muawyah Dawoud Al-Bdour
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):210-217 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.002 
A high awareness level of diabetic retinopathy was found among Jordanians but the knowledge level is only average. More focus on enhancing knowledge level of diabetic retinopathy should be a priority. With an increase in the educational level of Jordanians and other populations, awareness has increased though information/ education should be improved, particularly information from medical professionals. Enrichment of the social media and internet websites with evidence-based information about diseases by medical professionals may help in improving the situation. The authors assessed the knowledge of diabetic complications among unaffected individuals. This may assist in improving the general knowledge about DR and may also help in preventing diabetes.
Effect of treatment with carteolol and latanoprost in newly diagnosed primary open-angle glaucoma on peripapillary vessel densityOriginal papers
Jan Lestak, Martin Fus, Sarka Pitrova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):203-209 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.010 
This work evaluates the effect of carteolol and latanoprost on vessel density in the peripapillary area of the optic nerve head. These drugs were chosen for two reasons: latanoprost is recommended by the European Glaucoma Society as the first-line drug for glaucoma. Carteolol works on a different principle but should not have any ischemic effect on the vascular system of the eye. In a previous study, during a 5-year follow-up of patients receiving beta-blockers (carteolol) and prostaglandins (latanoprost), the authors demonstrated a greater progression of visual field changes with prostaglandins than with beta-blockers. This led them, with the introduction of OCT angiography, to investigate whether they could detect changes in the vessels of the posterior pole of the eye in early-stage and newly diagnosed cases of primary open-angle glaucoma. The results showed that only patients treated with carteolol experienced a statistically significant improvement in vessel density.
Enhancing the utility of chromosome 6 and 8 testing in uveal melanoma biopsiesOriginal papers
Veronika Matuskova, Pavla Hornackova, Marek Michalec, Lenka Zlamalikova, Kvetoslava Matulova, Michal Uher
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):196-202 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.018 
This article addresses the issue of chromosomal testing in patients with uveal melanoma. It is currently the only examination that can predict the development of metastases in patients with malignant uveal melanoma. The significance of chromosome 3 testing is unequivocal. This article deals with the testing of chromosomes 6 and 8 and their importance in predicting metastatic involvement. In a retrospective study, a cohort of 54 patients underwent testing of melanoma chromosome 6 and 8 from enucleated eyes. The authors demonstrated the importance of chromosome 8 abnormalities in patients without monosomy 3. The gain of chromosome 8, in fact, overturns the favourable prognosis of disomy 3. Currently, for the first time in the history of ophthalmology, a drug has been approved that extends survival in metastatic uveal melanoma. Chromosomal testing in samples of malignant melanoma is gaining significance.
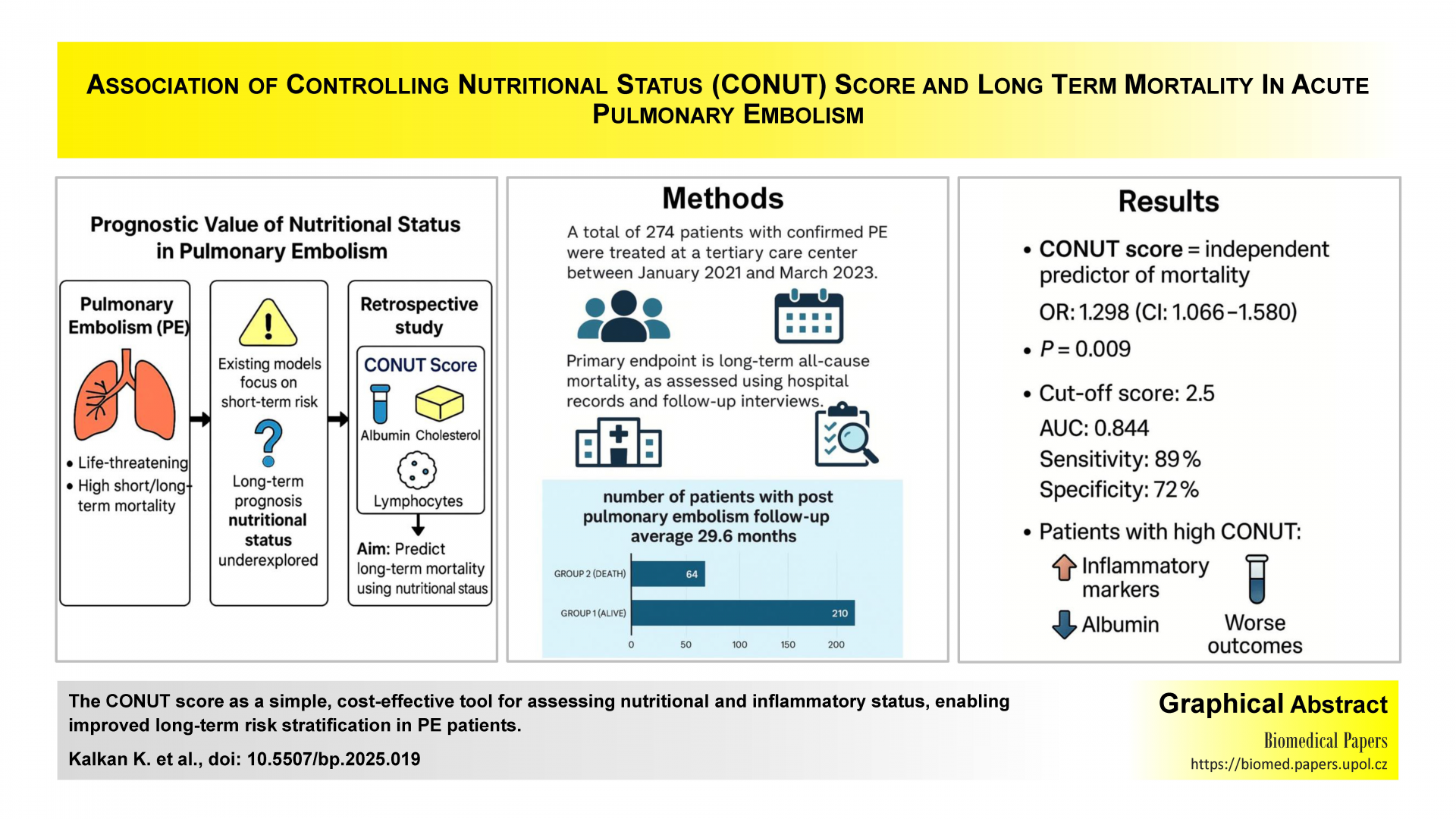
Association of controlling nutritional status score and long-term mortality in acute pulmonary embolismOriginal papers
Kamuran Kalkan, Cagatay Tunca, Veysel Ozan Tanik
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):188-195 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.019 
This study evaluates the prognostic relevance of the Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score in long-term mortality among patients with pulmonary embolism (PE). By integrating serum albumin, total cholesterol, and lymphocyte count, the CONUT score provides a comprehensive assessment of nutritional and immunological status. The findings suggest that the CONUT score may offer valuable insights for long-term risk stratification in PE, complementing existing clinical and biomarker-based approaches.
Dysfibrinogenemia and hypofibrinogenemia - Spectrum of pathogenic variants in Slovak patientsOriginal papers
Dominika Jaraskova, Jan Chandoga, Angelika Batorova, Tatiana Prigancova, Miriama Juhosova, Pavol Durina, Alzbeta Vavrova, Silvia Dallemule, Robert Petrovic, Anna Kyselova, Denisa Jankovicova, Daniel Bohmer
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):179-187 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.025 
Congenital hypofibrinogenemia (CH) and congenital dysfibrinogenemia (CD) are rare coagulation disorders caused by quantitative or qualitative defects in the fibrinogen gene. In this study, the authors, working to identify genetic variants and expanding knowledge about genetic variants in Slovak patients with congenital fibrinogen disorders registered at the National Haemophilia Centre. Molecular-genetic analysis have revealed six novel variants in 36 patients - FGA c.923_968dup p.(Gly324Lysfs*44) and FGG c.1105C>T p.(His369Tyr) were identified in CD patients. In CH patients, in the FGG gene c.8G>A p.(Trp3*), c.823G>T p.(Glu275*) and c.323C>A p.(Ala108Asp) variants were detected. In the FGB gene c.1427C>T p.(Ser476Leu) was identified.
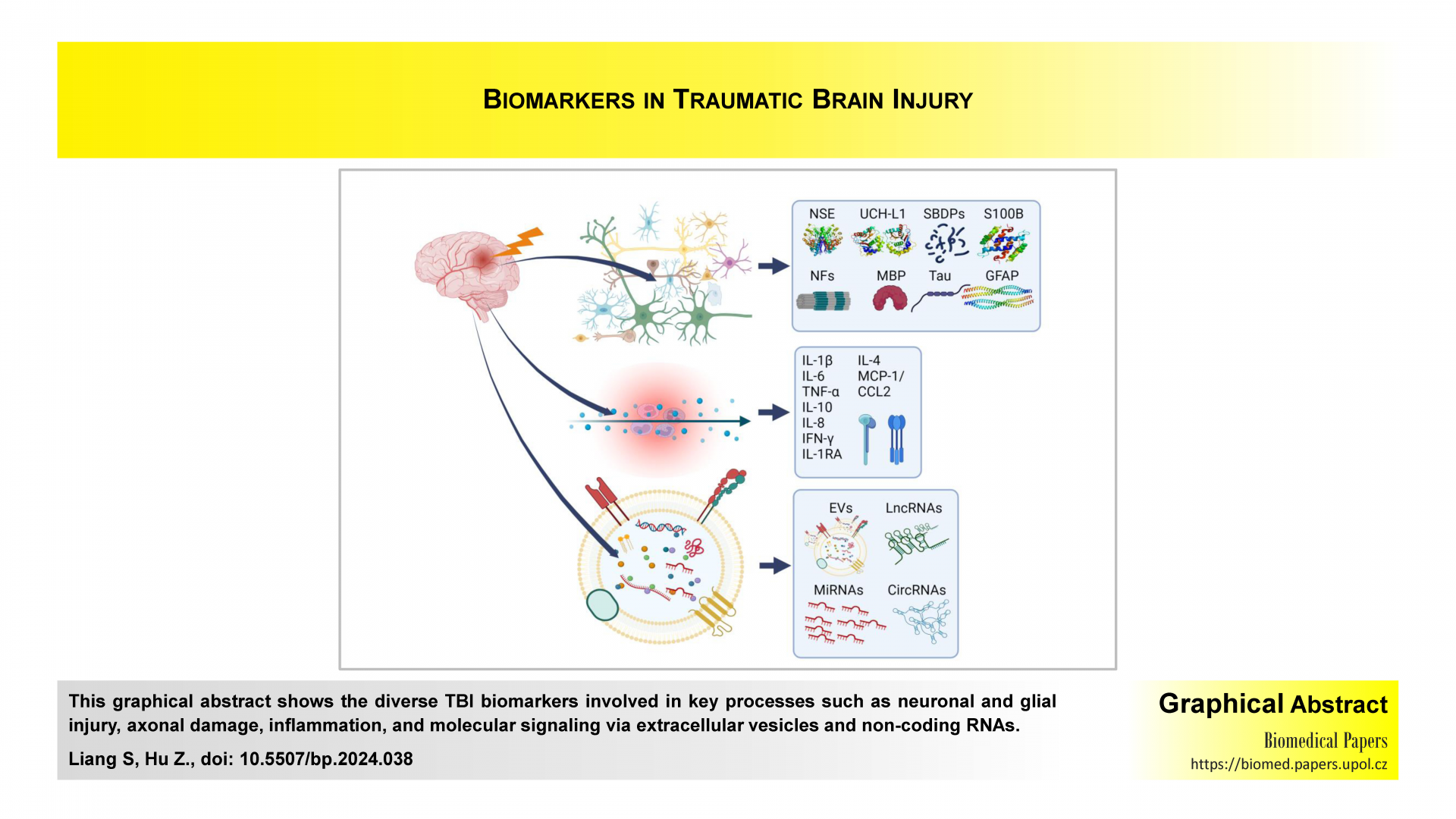
Unveiling the predictive power of biomarkers in traumatic brain injury: A narrative review focused on clinical outcomesReviews
Sitao Liang, Zihui Hu
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):161-178 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.038 
This review explores novel insights into the use of biomarkers for traumatic brain injury (TBI) prognosis and management. By examining emerging evidence on neuronal injury, inflammation, extracellular vesicles and non-coding RNAs, it underscores their potential in predicting clinical outcomes such as recovery and cognitive impairment. The work bridges a critical gap between basic research and clinical application, offering a comprehensive perspective on advancing diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for TBI.
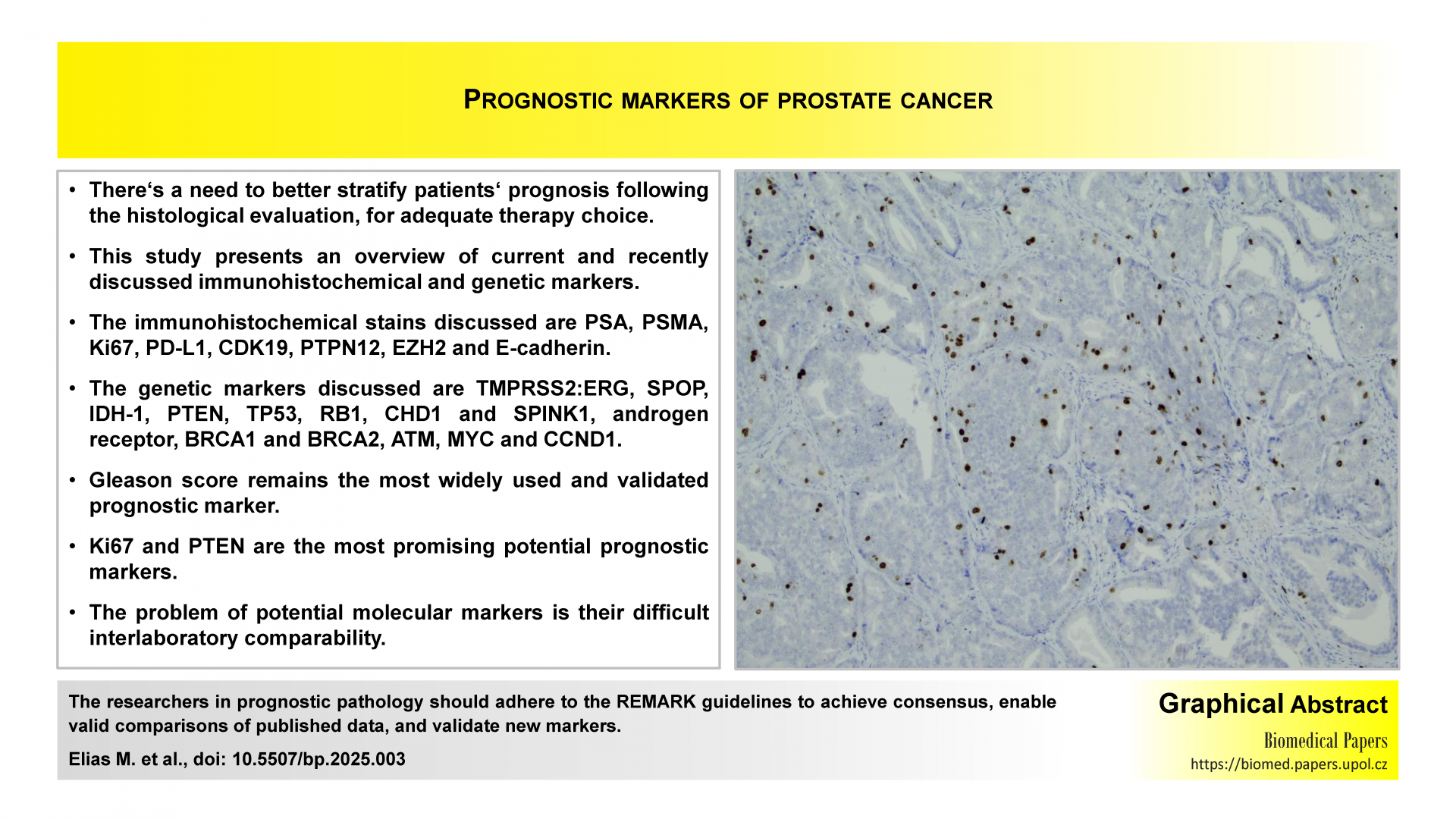
Contemporary review of prognostic markers of prostate cancer from a pathologist perspectiveReviews
Martin Elias, Jan Bouchal, Milan Kral, Daniela Kurfurstova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(3):149-160 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.003 
There is a current need to better stratify patient prognosis following histological evaluation for prostate cancer in order to optimise therapy decisions. In this article, the authors provide an overview of some recently discussed putative prognostic markers. These include the immunohistochemical stains PSA, PSMA, Ki67, PD-L1, CDK19, PTPN12, EZH2 and E-cadherin and the genes TMPRSS2:ERG, SPOP, IDH-1, PTEN, TP53, RB1, CHD1 and SPINK1, the androgen receptor, BRCA1 and BRCA2, ATM, MYC and CCND1. The results are not easy to interpret due to wide variations in a number of key variables. Overall, the Gleason score is still the most widely used and most validated of the prognostic markers. Ki67 and PTEN are the most promising.
Macular pigment evaluation using dual-wavelength fundus auto-fluorescence imagingOriginal papers
Patrik Rajs, Ivana Liehneova, Zbynek Stranak
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):144-148 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.051 
This study aimed to investigate changes in fundus autofluorescence in patients taking daily lutein oral supplements and to develop image processing methods for follow-up evaluations of the images. Dual wavelength fundus autofluorescence is a valuable technique for macular pigment evaluation in follow-up examinations, utilizing software image post-processing with commonly available hardware.
Peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer following vessel density correction at different IOP valuesOriginal papers
Jan Lestak, Martin Fus, Sarka Pitrova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):140-143 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.001 
In this study of early changes in glaucoma, the authors show that when the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) was reduced by correcting for vessel density (VD), there was a significant correlation between segments 5 (Superior Nasal) (r =-0.32, P<0.05) and 8 (Inferior Nasal) (r =-0.21, P<0.05) and degree of intraocular pressure. Use of this corrected RNFL from VD is a more appropriate method for detecting early changes in glaucoma. The above has been filed with the Patent and Invention Office under application number: PV 2023-234.
Determination of the prevalence and predictors of ventricular thrombus with assessment of the risk of systemic embolization to the CNS in patients after acute myocardial infarction using magnetic resonance imaging, echocardiography and cardiac markers - a prospective, unicentric, observational studyOriginal papers
Stepan Hudec, Martin Hutyra, Jan Precek, Jan Latal, Radomir Nykl, Miloslav Spacek, Martin Sluka, Daniel Sanak, Zbynek Tudos, Dalibor Pastucha, Milos Taborsky
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):132-139 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.050 
In this prospective, unicentric, observational study, the prevalence and predictors of left ventricular thrombus (LVT) formation after acute myocardial infarction (AMI) were investigated. The study aimed to assess the role of transthoracic echocardiography, cardiovascular magnetic resonance and cardiac markers in predicting LVT and to determine the risk of systemic embolization to the central nervous system using brain MRA. In a cohort of seventy patients, the prevalence of LVT detected by TTE was 15.9% and by DE-CMR was 16.7%. LVT prevalence was particularly high in patients with anterior STEMI. However, there was no significant association between LVT detection and the occurrence of cardioembolic events. These findings provide valuable insights into the diagnosis, prediction, and potential risk factors of LVT following AMI.
Oxidative stress, microparticles, and E-selectin do not depend on HIV suppressionOriginal papers
Katerina Havlickova, Svatava Snopkova, Miroslav Pohanka, Radek Svacinka, David Vydrar, Petr Husa Jr., Jirina Zavrelova, Filip Zlamal, Lenka Fabianova, Miroslav Penka, Petr Husa
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):123-131 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.002 
High levels of oxidative stress, E-selectin, and microparticles are detected in HIV patients with and without ART. These abnormalities predisposed to the diseases associated with aging. There were no correlations between these biomarkers and viral suppression that is detected in peripheral blood. These results support the hypothesis that residual viremia in cellular reservoirs of various tissues is the key factor related to the premature aging of the immune system.
Fat embolism and COVID-19 infection: autopsy and post-mortem laboratory findings in SARS-CoV-2 positive patientsOriginal papers
Adriana Gavronova, Lukas Hamerlik, Margita Bartkova, Vaclav Svrchokryl, Veronika Kralikova, Katerina Vranova, Peter Ondra, Martin Dobias
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):116-122 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.014 
During the COVID-19 pandemic, patients often died abruptly under the picture of circulatory and respiratory failure. The cause of this sudden deterioration remained hidden even after their death due to initial low number of the autopsies of COVID-19 positive patients. Fat embolism is a commonly overlooked cause of circulatory and respiratory failure, but it does not normally accompany viral infections and is therefore not standardly considered in their treatment. The authors present one of the first studies to relate these mechanisms based on microscopic examination with special staining of the specimens, shedding new light on the treatment of severe conditions of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Association of the combined parameters including the frequency of primary cilia, PD-L1, Smoothened protein, membranous β-catenin and cytoplasmic β-catenin expression with the outcome of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinomaOriginal papers
Aneta Rozsypalova, Blanka Rosova, Alzbeta Filipova, Dimitar Hadzi Nikolov, Renata Chloupkova, Igor Richter, Roman Zachoval, Radoslav Matej, Bohuslav Melichar, Tomas Buchler, Josef Dvorak
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):107-115 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.005 
The PD-L1, Smoothened protein and β-catenin expression were evaluated in 104 clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients (ccRCC). All studied tumor samples were acquired from nephrectomy specimens. An indirect immunohistochemistry was used. Median overall survival (OS) was significantly better in patients with lower PD-L1 expression (≤5%), Smoothened protein expression (<5%) or cytoplasmic β-catenin expression (≤75%) than in patients with higher expressions of these biomarkers (P<0.001, P=0.047, and P<0.001, respectively). Membranous β-catenin showed an opposite effect with its lower expression (≤75%) being associated with longer OS (P=0.020). The present study provides the first data on the potential association and combined prognostic significance of frequency of primary cilia, PD-L1, Smoothened protein and β- catenin expression with the outcome in ccRCC.
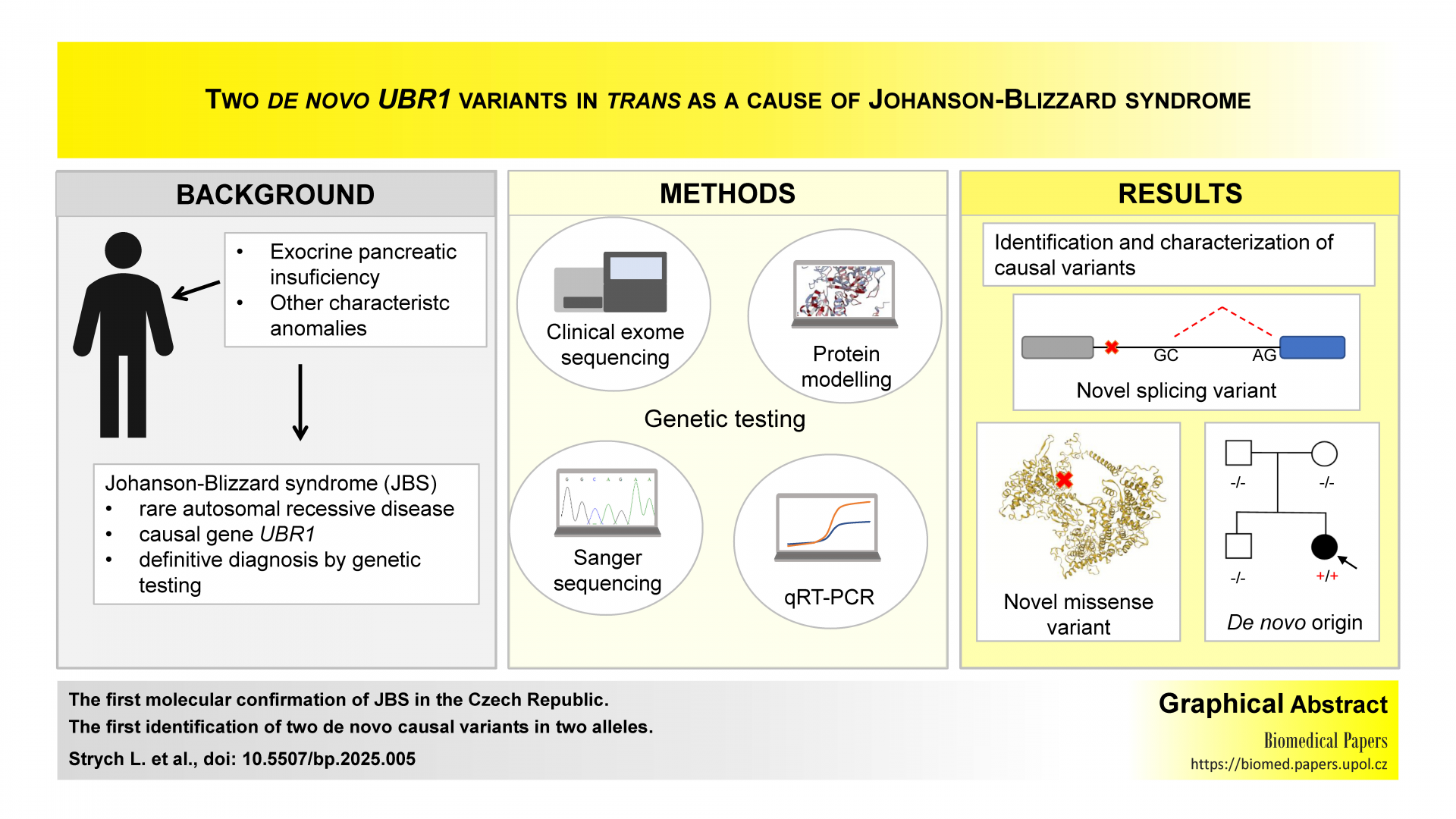
Two de novo UBR1 variants in trans as a cause of Johanson-Blizzard syndromeOriginal papers
Lukas Strych, Tomas Zavoral, Pavla Komrskova, Tomas Vanecek, Ivan Subrt
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):98-106 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.005 
The authors confirmed Johanson-Blizzard syndrome in a Czech proband by identification and characterization of two novel causal variants in the UBR1 gene (NM_174916.3), c.3482A>C and c.3509+6T>C. Using RNA and in silico analysis, they revealed that the splice site variant c.3509+6T>C induced the removal of a very rare non-canonical GC-AG intron and that the missense variant c.3482A>C altered a highly conserved zinc-coordinating histidine in the zinc-stabilized domain RING-H2. Although the variants were found in trans, neither was detected in the parents. To the best of their knowledge, the authors report the first molecular confirmation of JBS in the Czech Republic and the first identification of two de novo causal variants in two alleles.
Serum neurofilament light chain in response to probiotics in bi-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial (CleverAge Biota)Original papers
Lenka Fialova, Ales Bartos, Marta Kalousova, Libuse Noskova, Miroslava Zelenkova, Michaela Slukova, Tomas Zima
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):91-97 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.032 
Brain function could be influenced by probiotics through gut microbiota. For the first time, the effect of probiotics was assessed by monitoring the concentrations of the neurodegeneration biomarker neurofilament light chains (NfL) in a well-defined group of community-dwelling individuals. A three-month intervention with original probiotics was not reflected in a reduction of serum NfL concentrations. Monitoring serum NfL concentrations did not show significant axonal degeneration at a three-month interval in community-dwelling elderly without probiotic intervention.
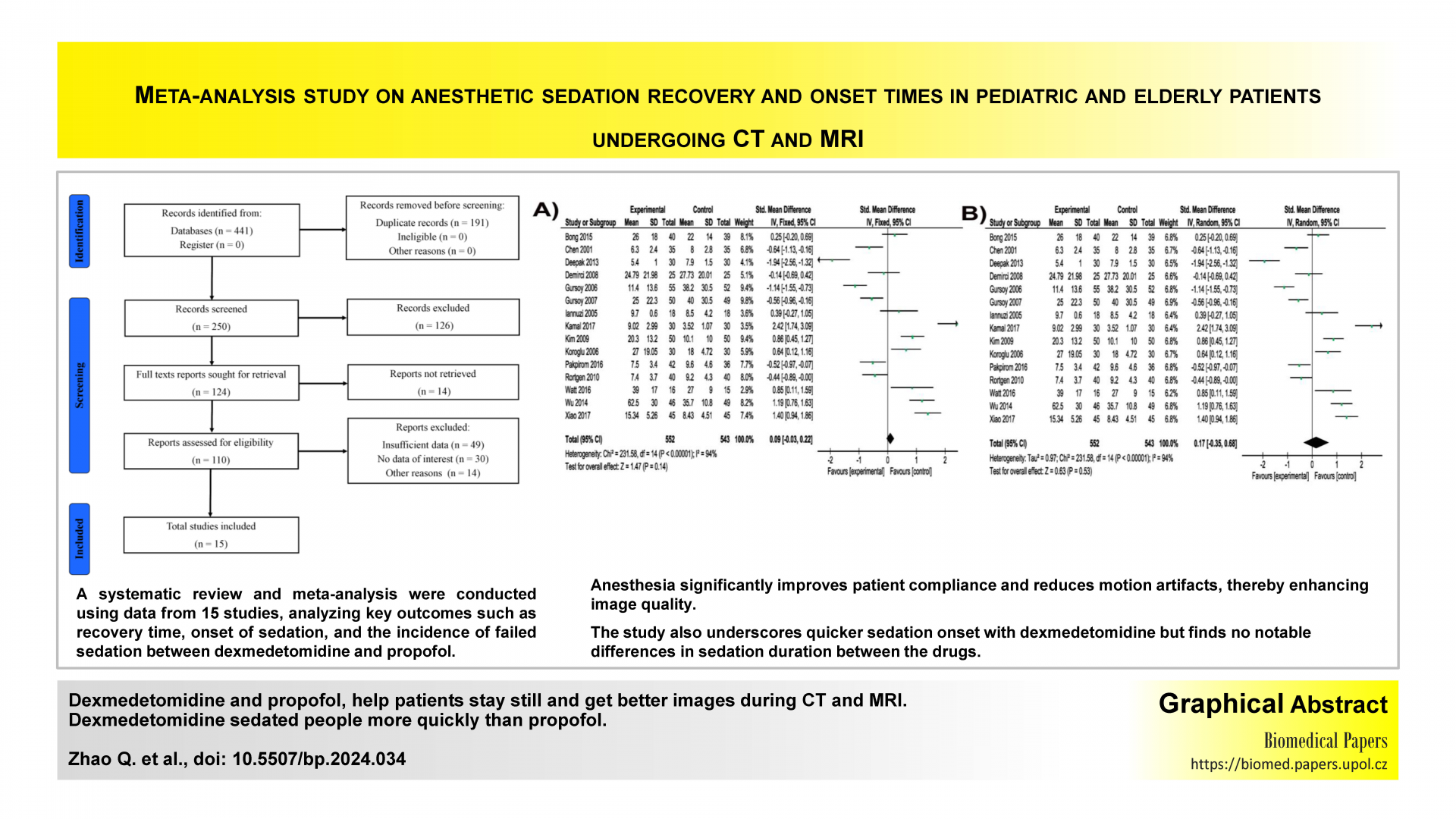
Meta-analysis study on anesthetic sedation recovery and onset times in pediatric and elderly patients undergoing CT and MRIReviews
Qiong Zhao, Fei Meng, Huimei Han, Lili Han
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):82-90 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.034 
This meta-analysis offers a comprehensive evaluation of anesthesia effectiveness, comparing dexmedetomidine and propofol, in pediatric and elderly patients undergoing CT and MRI procedures. It highlights original findings from a meta-analysis of 15 studies, demonstrating that anesthesia significantly improves patient compliance and reduces motion artifacts, thereby enhancing image quality. The study also underscores quicker sedation onset with dexmedetomidine but finds no notable differences in sedation duration between the drugs. Despite these promising results, the high heterogeneity in outcomes calls for further research to refine anesthesia strategies for optimal patient care
Adrenal insufficiency - causes and laboratory diagnosisReviews
Tomas Brutvan, Jana Jezkova, Marcela Kotasova, Michal Krsek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(2):73-81 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.033 
This article provides an overview of the causes of adrenocortical insufficiency, characteristic laboratory findings, and hormonal examinations including stimulation tests used in diagnostics. Attention is given to factors that may influence the results of hormonal examinations as well as to individual methods of laboratory determination. A special section within the article is dedicated to the use of plasma cortisol determination using liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), drawing on our own experiences.
Study protocol - Prospective case-control trial - Impact of significant carotid stenosis on retinal perfusion measured with automated retinal oximetryOriginal papers
Petr Polidar, Barbora Paskova, Marta Karhanova, Martin Sin, Tomas Dornak, Zuzana Schreiberova, Petra Divisova, Tomas Veverka, David Franc, Daniel Sanak, Michal Kral
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(1):66-71 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2023.052 
The manuscript describes the protocol for a prospective study evaluating the relationship between carotid stenosis and retinal oxygen metabolism. Carotid stenosis is a major cause of ischaemic stroke worldwide. Retinal oximetry imaging of retinal blood vessels is noninvasive and capable of direct examination of the post-stenotic blood flow. It may be useful in differentiating high and low risk stenosis of the same severity. The results will yield more information about adaptive changes in the post-stenotic basin and may reveal mechanisms behind larger ischaemic deficits in some stroke patients. Previous studies have demonstrated that retinal blood flow is affected in a variety of eye and systemic diseases, including diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration, and glaucoma.



