Biomedical papers, 2025 (vol. 169), issue 4
Reviews
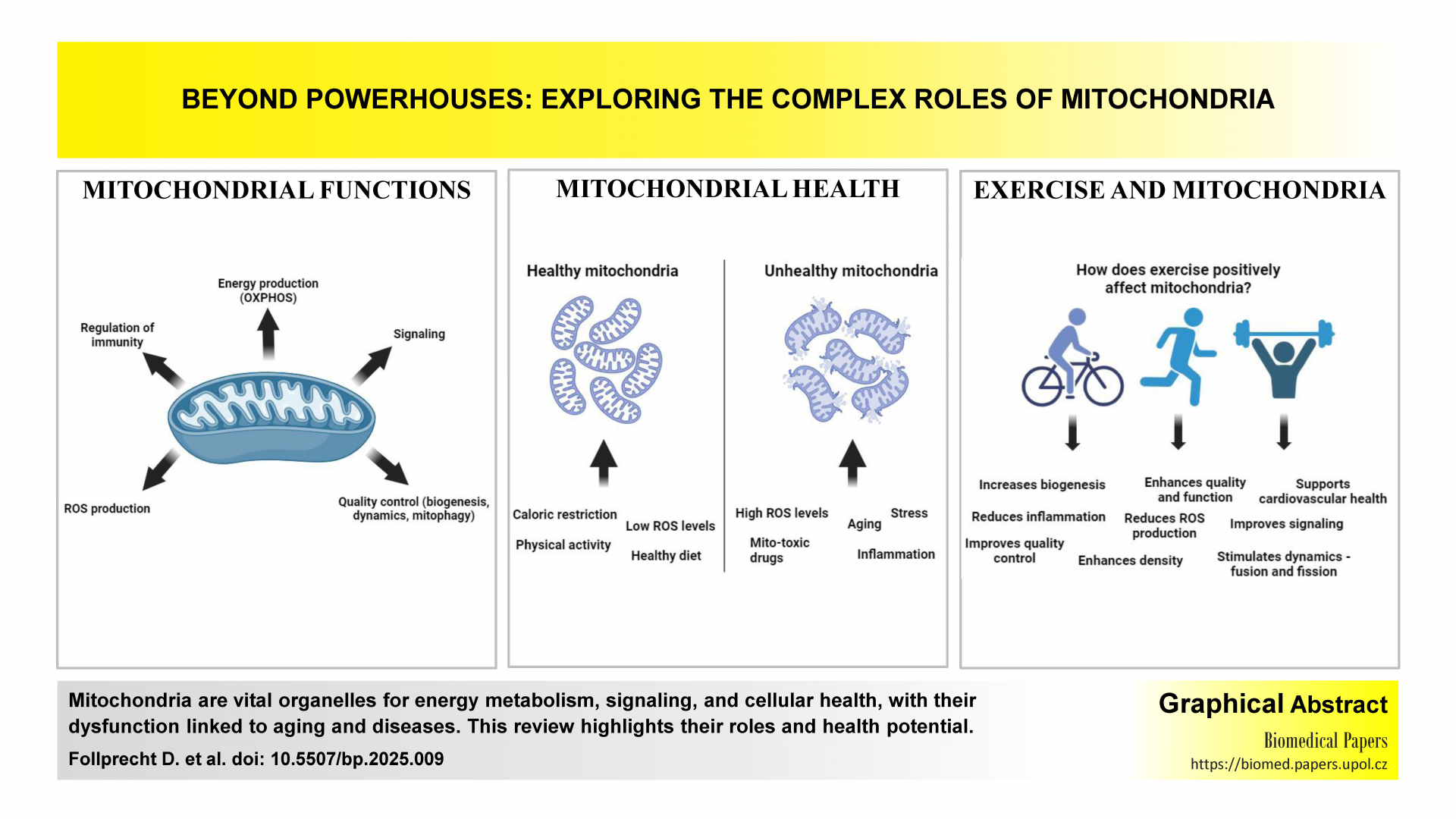
Mitochondria in focus: From structure and function to their role in human diseases. A review
Daniel Follprecht, Jakub Vavricka, Viktorie Johankova, Pavel Broz, Ales Krouzecky
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):235-246 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.009 
This work provides an in-depth exploration of mitochondrial functions beyond energy production, highlighting their essential roles in cellular processes, signaling, and health maintenance. By emphasizing recent advances in mitochondrial research, the manuscript underscores the impact of mitochondria in aging, disease, and exercise, offering valuable insights that could guide therapeutic strategies for enhancing mitochondrial health and longevity
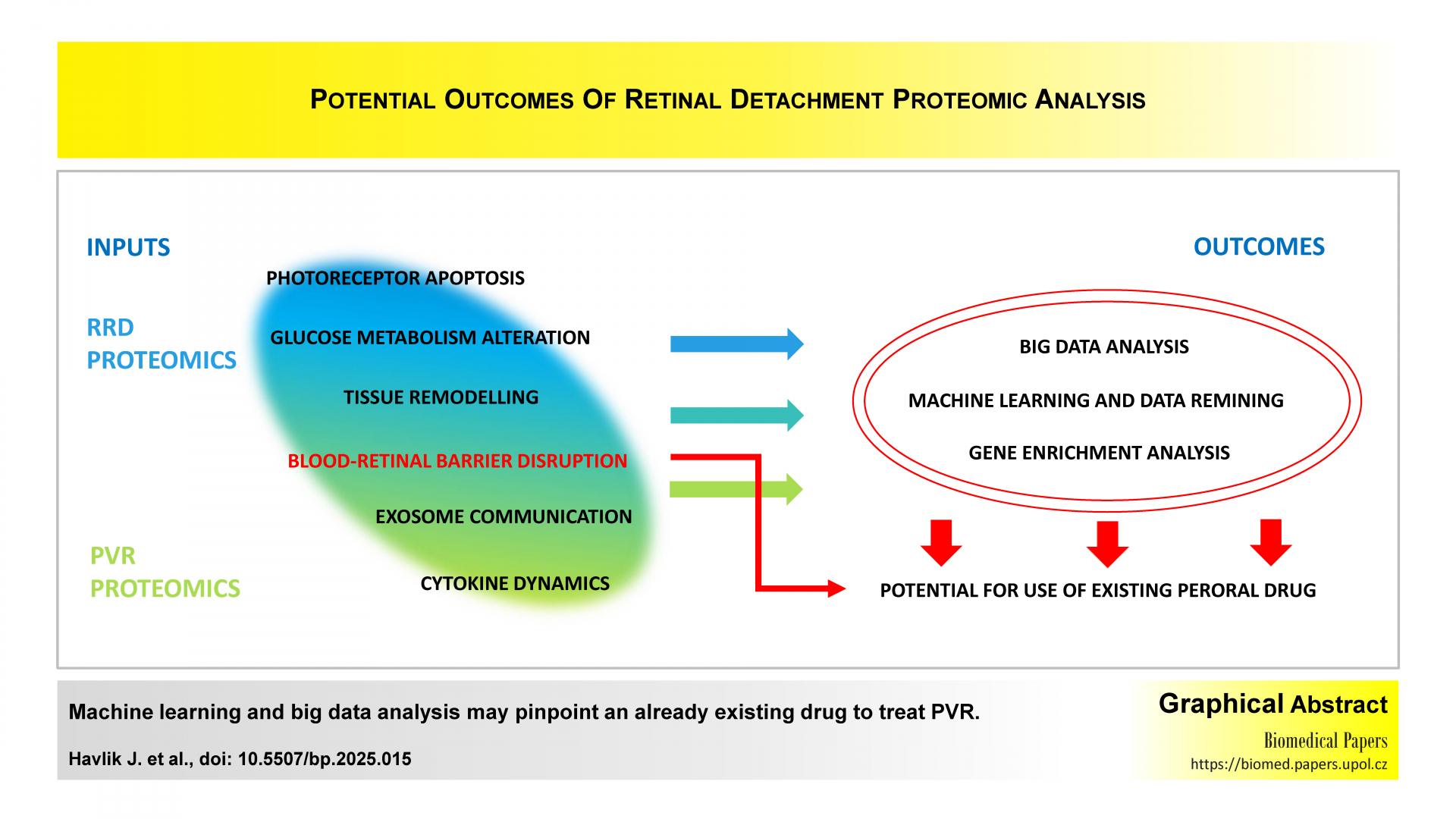
Vitreous proteomics in rhegmatogenous retinal detachment and proliferative vitreoretinopathy
Jan Havlik, Martin Lada, Jan Tesar, Vladimir Kratky, Martin Sin
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):247-254 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.015 
Proteomic analysis of the vitreous has unveiled critical molecular mechanisms underlying retinal pathologies, highlighting novel therapeutic opportunities. This study explores the dynamic protein changes associated with detachment-induced photoreceptor degeneration, metabolic stress, and inflammation. Key findings reveal altered glycolytic enzymes, antioxidant depletion, and cytokine dysregulation, underscoring their roles in cellular damage and repair. The review emphasizes the transformative potential of advanced proteomics, such as data-independent acquisition and exosome profiling, in identifying biomarkers and therapeutic targets, paving the way for precision medicine in combating vision-threatening conditions.
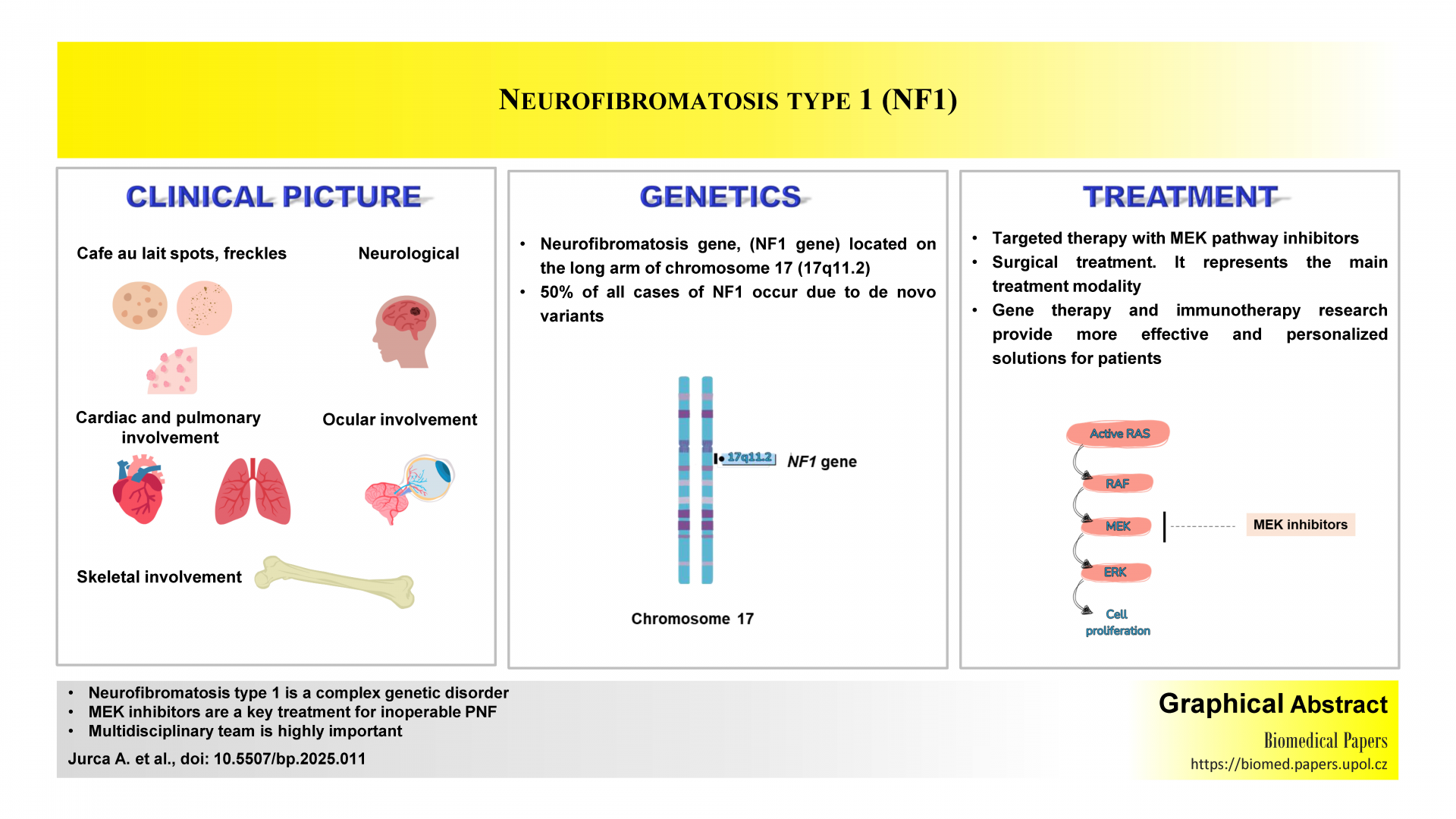
Unveiling the complexity of neurofibromatosis type 1: Innovations in genetic understanding and clinical management. A narrative review
Aurora Jurca, Simona Pop, Claudia Maria Jurca, Cosmin Mihai Vesa, Alexandru Daniel Jurca
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):255-261 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.011 
This narrative review offers a unique perspective on recent advances in the genetics, diagnosis, and management of neurofibromatosis type 1. Unlike previous studies, it incorporates the updated 2021 NIH criteria, emphasizing the role of genetic testing for early diagnosis and personalized treatment. The article highlights genotype-phenotype correlations, the impact of specific mutations on disease severity, and the need for continuous monitoring. It also covers less commonly addressed aspects, such as the increased breast cancer risk in women with NF1, emerging therapies like MEK inhibitors, and the importance of tailored surveillance, making it a valuable contribution to NF1 management.
Original papers
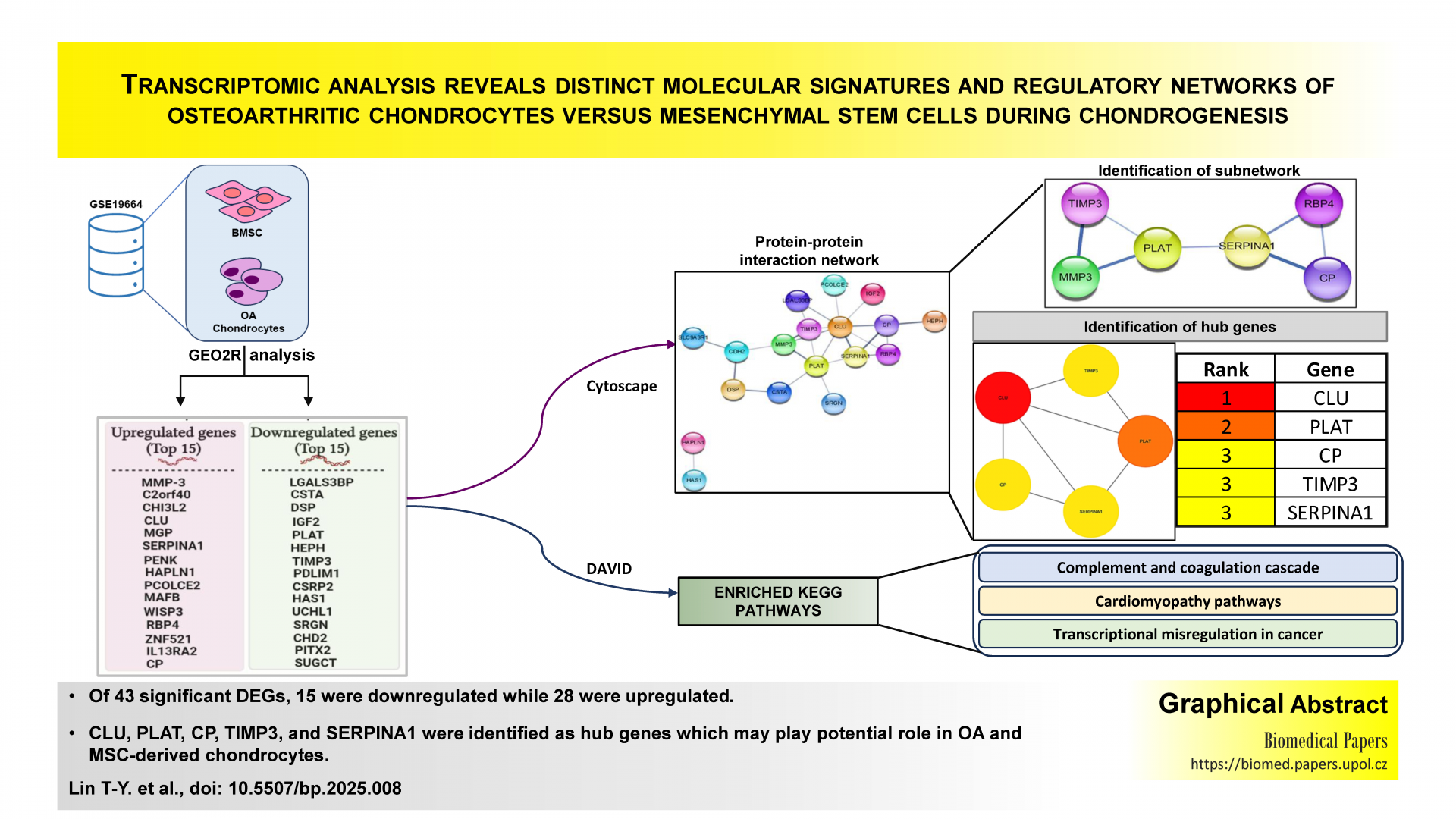
Transcriptomic analysis reveals distinct molecular signatures and regulatory networks of osteoarthritic chondrocytes versus mesenchymal stem cells during chondrogenesis
Tsung-Yu Lin, Viraj Krishna Mishra, Rajni Dubey, Thakur Prasad Chaturvedi, Shankar Narayan A, Hsu-Wei Fang, Lung-Wen Tsai, Navneet Kumar Dubey
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):262-271 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2025.008 
This bioinformatics study aimed to determine differentially expressed genes (DEGs) patterns of knee osteoarthritis chondrocytes versus human bone marrow stem cells towards chondrogenic commitment. We identified 43 DEGs (15 downregulated and 28 upregulated) and enriched pathways, which revealed the enrichment of complement and coagulation cascades and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy pathways for upregulated and downregulated DEGs, respectively. Hub networks identified the top 5 hub genes, including CLU, PLAT, CP, TIMP3, and SERPINA1.
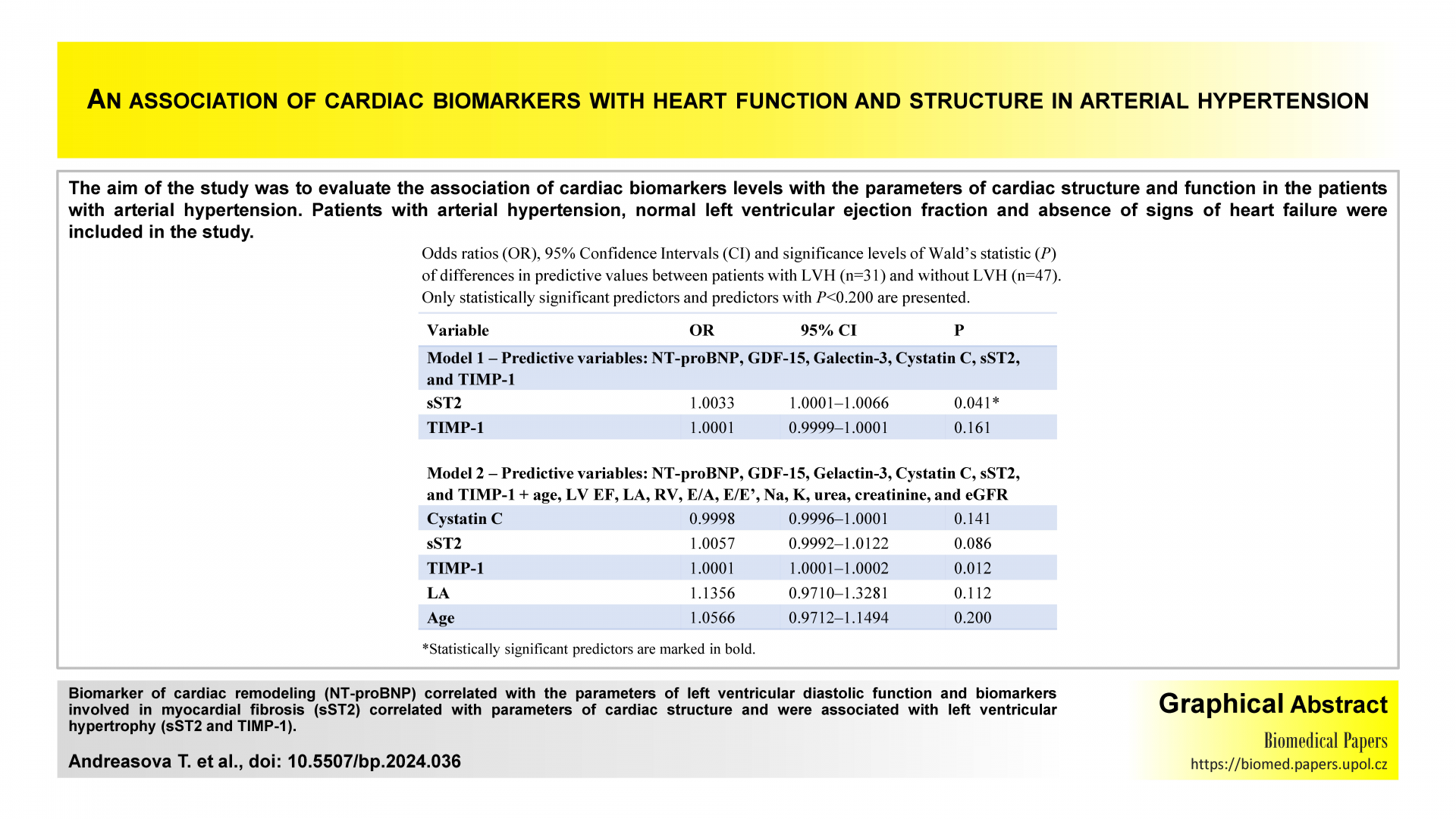
Association of biomarkers of cardiac remodeling, myocardial fibrosis and inflammation with parameters of heart function and structure in patients with arterial hypertension
Tana Andreasova, Filip Malek, Zuzana Jiraskova Zakostelska, Petr Neuzil, Jana Vranova
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):272-280 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.036 
The aim of the study was to evaluate the association of cardiac biomarkers levels with the parameters of cardiac structure and function in the patients with arterial hypertension. Patients with arterial hypertension, normal left ventricular ejection fraction and absence of signs of heart failure were included in the study. Biomarker of cardiac remodeling (NT-proBNP) correlated with the parameters of left ventricular diastolic function and biomarkers involved in myocardial fibrosis (sST2) correlated with parameters of cardiac structure and were associated with left ventricular hypertrophy (sST2 and TIMP-1).
Comparison of myocardial perfusion study and invasive hemodynamic measurement of the significance of non-infarct-related residual stenoses in ST elevation myocardial infarction patients
Jan Vacha, Miloslav Spacek, Milan Kaminek, Martin Hutyra, Radomir Nykl, Martin Sluka, Milos Taborsky
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):281-287 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.021 
The authors present the results of their study focused on patients with acute STEMI and multivessel coronary artery disease. Fractional flow reserve (FFR) guided staged intervention of the so far silent non-IRA lesions (50-90%) was performed 4-8 weeks after STEMI closely preceded by myocardial perfusion study (MPS). We offer a comparative analysis of these methods within real-world scenarios. The major finding was that they observed weak correlation in ischemia detection between MPS using SPECT and invasive hemodynamic measurement using FFR. In patients with abnormal myocardium detected by MPS significantly lower FFR values were observed in the non-IRAs compared to patients with negative MPS studies. Further studies are needed to guide the optimal treatment strategy in such patients.
The role of Fetuin-A and Leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein in the diagnosis of prostate cancer - a pilot study
Alena Sorokac Kubolkova, Gabriel Varga, Miroslava Benovska, Lenka Kovacova, Michal Fedorko
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):288-292 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.028 
In recent years, several studies have been conducted to develop different biomarkers of prostate cancer with high sensitivity and specificity. Minimal studies have so far focused on Fetuin-A and Leucine-rich α-2-glycoprotein (LRG1) as potential biomarkers for prostate cancer. This article reports on these 2 potential biomarkers, that have been investigated in their department and can help in future screening for early detection and diagnosis, reduce the number of unnecessary biopsies, assess the risk of aggressive disease, and monitor response to prostate cancer treatment. Through this study, Fetuin-A has proven to be a potential new biomarker for prostate cancer.
Urinary tract trauma as a predictor of acute kidney injury in severely injured patients: A retrospective analysis of observational studies
Michal Frelich, Jan Pavlicek, Filip Bursa, Vojtech Vodicka, Dana Salounova, Peter Sklienka
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):293-297 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.026 
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of the most common organ dysfunctions in major trauma. Patients with multiple injuries are exposed to several risk factors for AKI, including haemorrhage, systemic inflammation, rhabdomyolysis, and secondary insults from emergency surgery and infection. Because the development of AKI is associated with multiple adverse outcomes, such as increased length of hospital stay, mortality, and total cost of healthcare, it is essential to identify all risk factors early and, in indicated cases, initiate preventive measures with the aim of reducing the incidence of AKI and subsequent complications. Although it seems intuitive that direct injury to the urinary tract would affect its function, very little is known about the risk of AKI in this setting. In this study, the authors demonstrated that injury to the urinary tract was an independent predictor of the development of AKI with an RR of 3.4 (95% CI 2.25-5.06), whereas injury to the kidneys or their vascular supply resulted in a threefold increased risk of AKI (RR = 3.1, 95% CI 1.93-4.90), and injury to the urinary passages had an RR of 4.2 (95% CI 2.70-6.46). Based on AUC ROC curve analysis, the authors found that NGAL levels measured within 24 h of admission were a reliable predictor of AKI only in patients without urinary tract injury.
Case report
Primary ventriculitis caused by Streptococcus intermedius - a rare case and challenge with uncertain clinical outcome. Case report
Stefan Trnka, Premysl Stejskal, Jakub Jablonsky, David Krahulik, Eva Cechakova, Lumir Hrabalek
Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2025, 169(4):298-300 | DOI: 10.5507/bp.2024.029 
This case report presents a unique instance of primary ventriculitis in a 53-year-old patient with no predisposing factors, caused by the rare pathogen Streptococcus intermedius. Despite early and targeted antibiotic therapy, the patient's condition did not improve, highlighting the challenges in managing such infections. Imaging studies and cerebrospinal fluid analysis were crucial for diagnosis, revealing significant inflammation and ventricular debris. This case emphasizes the need for further research into the treatment of primary ventriculitis, as standard therapeutic approaches may not always be effective. The findings underscore the importance of early detection and the complexity of managing central nervous system infections.
This issue was published with support of Zentiva company




